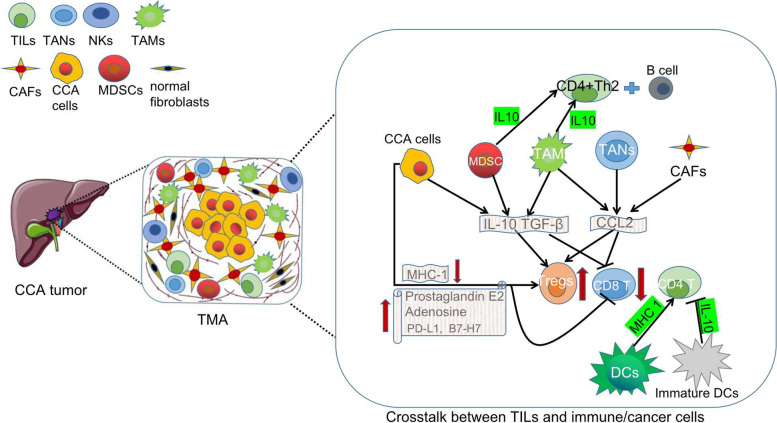
Fig. 4.
Overview of the crosstalk between TILs and immune/cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment Cancer cells, TAMs and MDSCs emit IL-10 and TGF-β, while TAMs, TANs and CAFs secrete CCL2 which attracts and expands Tregs inside the tumor bed and inhibits the activity of CD8+T cells. Cancer cells can also directly impair the immunoresponse by overexpressing prostaglandin E2, adenosine, PD-L1 or B7-H7 or by lowering MHC-I surface expression. IL10 released by MSDCs and TAMs favors a CD4+ Th2 response with B-cell engagement which are both effective cancer immunosurveillance mechanisms. Mature DCs promote CD4+ T cell activity by increasing MHC 1 expression while immature DCs inhibit CD4+ T activity by secreting IL-10. B7-H7, B7 homolog 7; CAFs, Cancer-associated fibroblasts; CCL,C–C motif chemokine ligand; CD, cluster of differentiation; DCs, Dendritic cells; IL, interleukin; MDSCs, Myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MHC; major histocompatibility complex; PD-L1, Programmed death-ligand 1; TANs, tumor associated neutrophils; TAMs, tumor-accociated macrophages; TGF, transforming growth factor; Tregs, Regulatory T cells