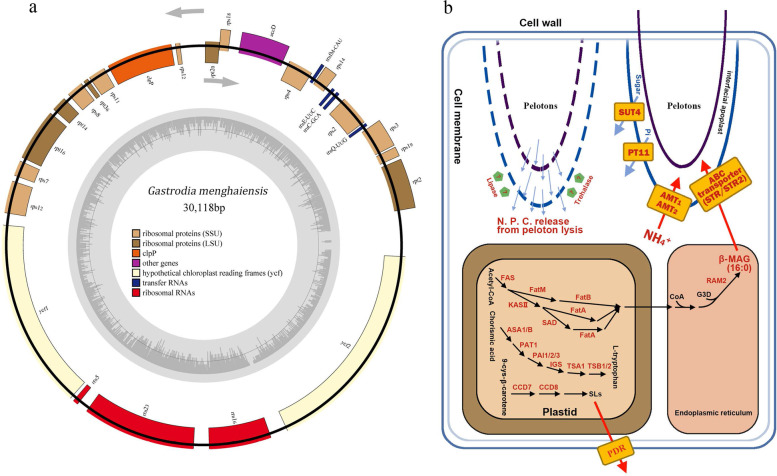
Fig. 4.
Plastid genome of G. menghaiensis and proposed model of biological interaction between G. menghaiensis and symbiotic fungi. a The plastid genomes of G. menghaiensis. SSU, small subunit; LSU, large subunit. b Model of biological interaction between G. menghaiensis and symbiotic microbials. ASA1/B, anthranilate synthase; PAT1, phosphoribosyl tranferase; PAI1/2/3, PRA isomerase; IGS, InGP synthase; TSA1, Trytophan synthase; TSB1/2, Trytophan synthase; SLs, Strigolactone; FAS, fatty acid synthase; KASII, ketoacyl-ACP synthase II; SAD, stearoyl-ACP desaturase; FatA, acyl-ACP thioesterase A; FatB, acyl-ACP thioesterase B; FatC, acyl-ACP thioesterase C; FatM, acyl-ACP thioesterase M; ABC transporter, ATP binding cassette transporter; CoA, coenzyme A; MAG, monoacylglycerol; SUT4, sugar transporter 4; PT11/PT4, Phosphorus transporter 11; AMT1, AMT4, ammonium transporters 1 and 4; CCD 7, CCD 8, carotenoid cleavage dioxygenases; PDR, ATP binding cassette transporter. The schematic diagrams of strigolactone, monoacylglycerol and L-trytophan pathway were edited according to KEGG and reported references [9, 46, 47]