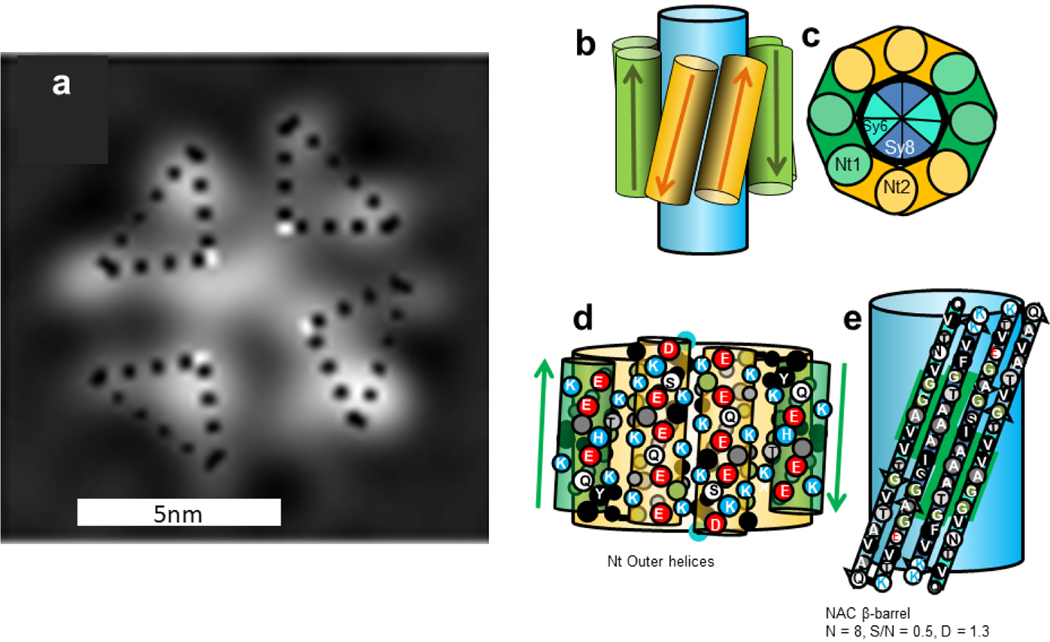
Figure 5.
(a) EM images of fractionally occupied helical tetramer with 2- or 4-fold symmetry, Copied with permission from Wang et al. [41], and (b-e) schematics of an αβ-barrel Type 2 tetramer model for α-Syn. (b) The model viewed from the side; the large blue cylinder represents the NAC β-barrel. (c) Wedge representation of a cross-section of four Nt helical hairpins surrounding an eight-stranded antiparallel β-barrel formed by four NAC β-hairpins. (d) Representation of Nt helices for two subunits superimposed on the Nt helical-barrel. (e) Flattened representation of two NAC β-hairpins superimposed on a light blue β-barrel. The Sy7 hairpin is not present in β-Syn, but it is preceded and followed by residues that are identical in α- and β-Syn (green background). The larger circles represent side-chains oriented outwardly on the front side of the helices or strands, the smaller circles are for those on the back side. Side-chains are colored by their properties: hydrophobic side-chains (V, I, L, M,F, Y) are black with white letters, less hydrophobic alanine is dark gray with white letter, glycine is green with white letter, ambivalent threonine is light gray with black letter, uncharged hydrophilic S, Q, and N, are white with black letter, negatively charged D and E are white with red letters, positively charged K and R are white with blue letters, sometimes positively charged H is light gray with blue letter. The N and C terminal residues are outlined in blue and red to indicate their positive and negative charges. The number of β-strands, N; sheer number to N ratio, S/N; and diameter of backbone, D, are listed below the NAC β-barrel.