Figure 3. Selective TRPV4 agonists induce cation currents in retinal microglia.
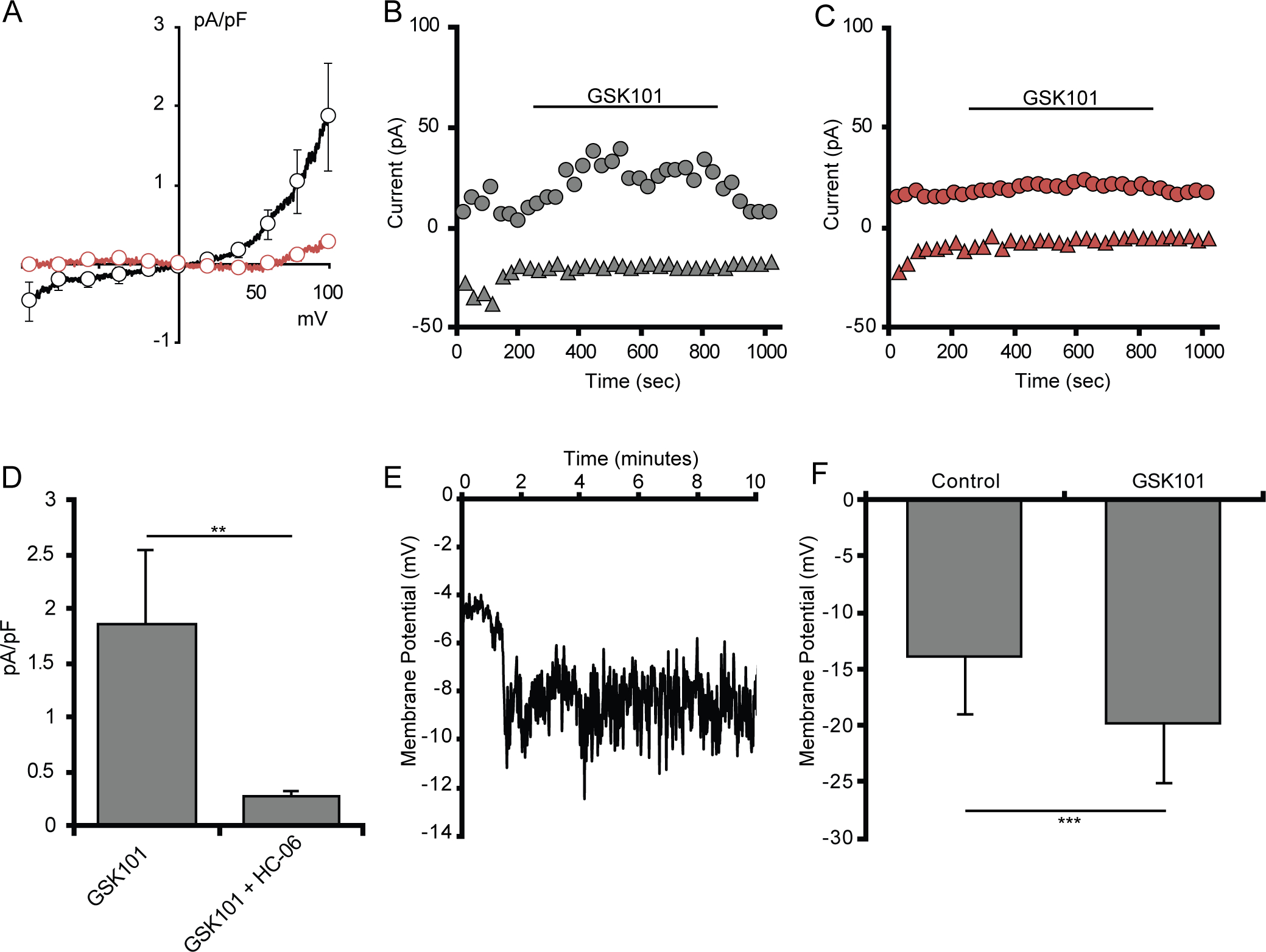
(A) Average I-V curve of GSK101-induced currents in acutely dissociated microglia (n = 4). (B) Average I-V curve of GSK101-induced currents in in situ microglia either untreated (n = 6, black trace) or treated with HC-06 (n = 6, red trace). GSK101-induced currents were obtained by subtraction of the currents before GSK101 application from the currents at the maximum response to GSK101. (C) Representative time course of whole-cell currents in an untreated microglia (gray) or a microglia pretreated with HC-06 (red) at 100 mV (circles) and −100 mV (triangles). (D) Quantification of GSK101-induced currents in in situ microglial cells untreated and treated with HC-06 (baselines currents were subtracted), with current amplitude values at −100 mV. (E) Quantification of GSK101-induced currents in dissociated microglial cells. (F) Representative trace of dissociated microglial membrane potential hyperpolarizing in response to GSK101. (G) Quantification of the change in membrane potential of retinal microglia (n = 4) exposed to GSK101. All values are represented as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical significance was determined with a paired-sample t-test, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
