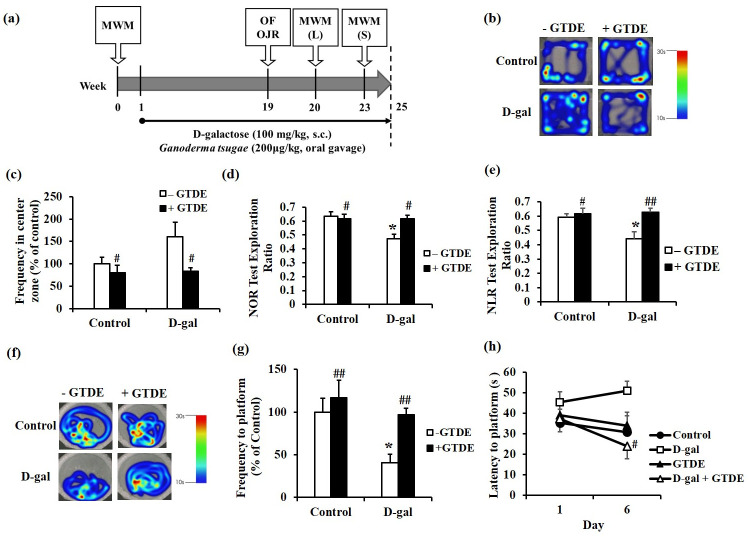
Fig 1. GTDE restored recognition memory against d-gal induced aging.
The rats received daily drug administrations based on group assignments. D-gal was administered by subcutaneous injection at a dose of 100 mg/kg/day, and GTDE was administered orally at a dose of 200 μg/kg/day. Rats in the control group received equivalent volumes of the solvent. At 18 weeks after the commencement of drug administration, the rats were subjected to the open-field test ((b), (c)), object recognition test ((d), (e)), and Morris water maze test ((f) to (h)). (a) The detailed experimental schedule. (b) The heat map for the open-field test, with red denoting the maximum duration of stay of 30 s and blue denoting the minimum duration of 10 s. (c) The quantified frequencies at which the rats reached the central zone. (d) Results of the NOR test. (e) Results of the NLR test. (f) Heat map for the Morris water maze test, with red denoting the maximum duration of stay of 30 s and blue denoting the minimum duration of 10 s. (g) Quantified frequencies of platform exploration during the long-term memory test. (h) Results of the working memory test. Intergroup differences were compared using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Statistically significant differences based on comparisons with the control group are denoted by *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; statistically significant differences based on comparisons with the D-gal group are denoted by #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001. n = 7 per group.