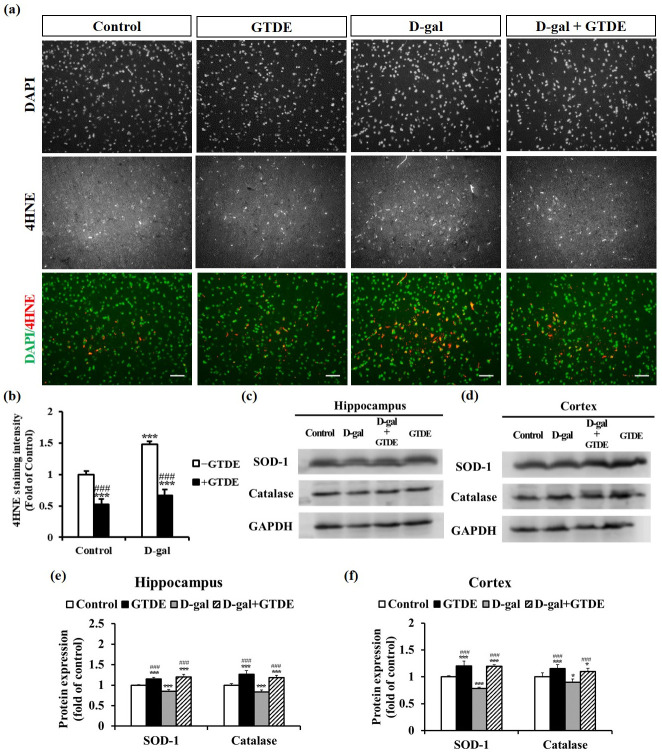
Fig 3. GTDE effectively reduced d-gal-induced oxidative stress and increased the expression levels of antioxidant proteins and BDNF.
(a) Expression of the lipid peroxidation product 4-HNE in the cerebral cortical sections of the rats (scale bar = 50 μm). n (images) value = 21 (control); 20 (GTDE); 23 (D-gal); 21 (D-gal+aging). (b) Quantitative results of 4-HNE staining intensity. (c) to (f) Western blots of the proteins obtained from the homogenization of the hippocampal and cerebral cortical tissues of the rats. The changes in SOD-1 and catalase expressions were compared with the use of GAPDH as the loading control. n = 9. (c) and (d) Representative western blots for the hippocampus and cerebral cortex, respectively. (e) and (f) Corresponding quantified results. Intergroup differences were compared using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Statistically significant differences based on comparisons with the control group are denoted by *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; statistically significant differences based on comparisons with the D-gal group are denoted by #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001.