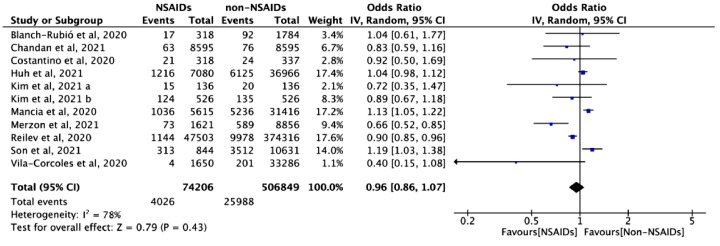
Figure 4.
The association between NSAID exposure and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients who were negative to SARS-CoV-2 tests during the COVID-19 pandemic. “Events” is the number of SARS-CoV-2 infection; “Total” is population size; “Weight” is study weight in the analysis. “IV” is inverse variance statistical method of meta-analysis; “Random” is random effects model; “95% CI” is the 95% confidence intervals for the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection; Each horizontal line in the graphical display represents a study, its width represents 95% CI of the interval estimation of the odds ratio effect of risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and the blue midpoint of the line symbolizes the point estimate of the unadjusted odds ratio effect of risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection; “I2” represents the quantity of heterogeneity (0–100%); “Test for overall effect: Z = 0.79 (P = 0.43)” confirms no statistical difference illustrated by the diamond crossing the line of effect (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).