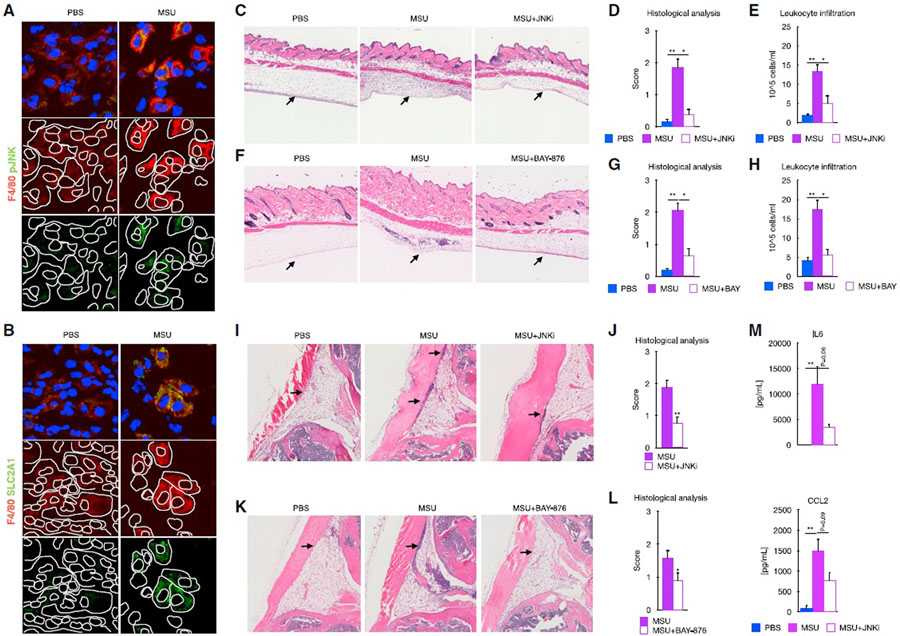
Figure 7. Signaling by JNK and SLC2A1 is required for the MSUc-induced damage in vivo.
(A and B) Protein analysis by IF showing expression of SLC2A1 (A) and pJNK (B) in macrophages in the subcutaneous cavity of the air pouch when injected with MSUc for 8 h(n = 2/group). Signal for specific antibodies is pseudocolored in red. DAPI in blue is used to delineate DNA structures.
(C) Histological analysis by H&E is showing the recruitment of inflammatory cells (arrows) induced by MSUc in the air pouch is reduced upon treatment with JNKi (15 mg/kg; n ≥ 4/group).
(D and E) Pathological assessment of inflammatory cell infiltrates of the air pouch (D) and neutrophil count of the air pouch lavage (E) showing reduction in MSUc + JNKi versus MSUc (n ≥ 4/group).
(F) Histological analysis by H&E is showing the recruitment of inflammatory cells (arrows) induced by MSUc in the air pouch is reduced upon treatment with BAY-876 (5 mg/kg; n ≥ 5/group).
(G and H) Pathological assessment of inflammatory cell infiltrates of the air pouch (G) and neutrophil count of the air pouch lavage (H) showing reduction in MSUc + BAY-876 versus MSUc (n ≥ 10/group).
(I and J) Histological analysis by H&E showing reduction in the recruitment of inflammatory cells (arrow) in the synovial cavity of mice injected with MSUc + JNKi (15 mg/kg) versus MSUc (n ≥ 10/group).
(K and L) Histological analysis by H&E showing reduction in the recruitment of inflammatory cells (arrow) in the synovium of mice injected with MSUc + BAY-876 (7.5 mg/kg) versus MSUc (n ≥ 7/group). (M) Protein analysis by ELISA of serum levels of IL-6 or CCL2 in mice injected with MSUc w/wo JNKi in the air pouch showing reduction in MSUc + JNKi versus MSUc (n = 4/group) (#p < 0.10, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).