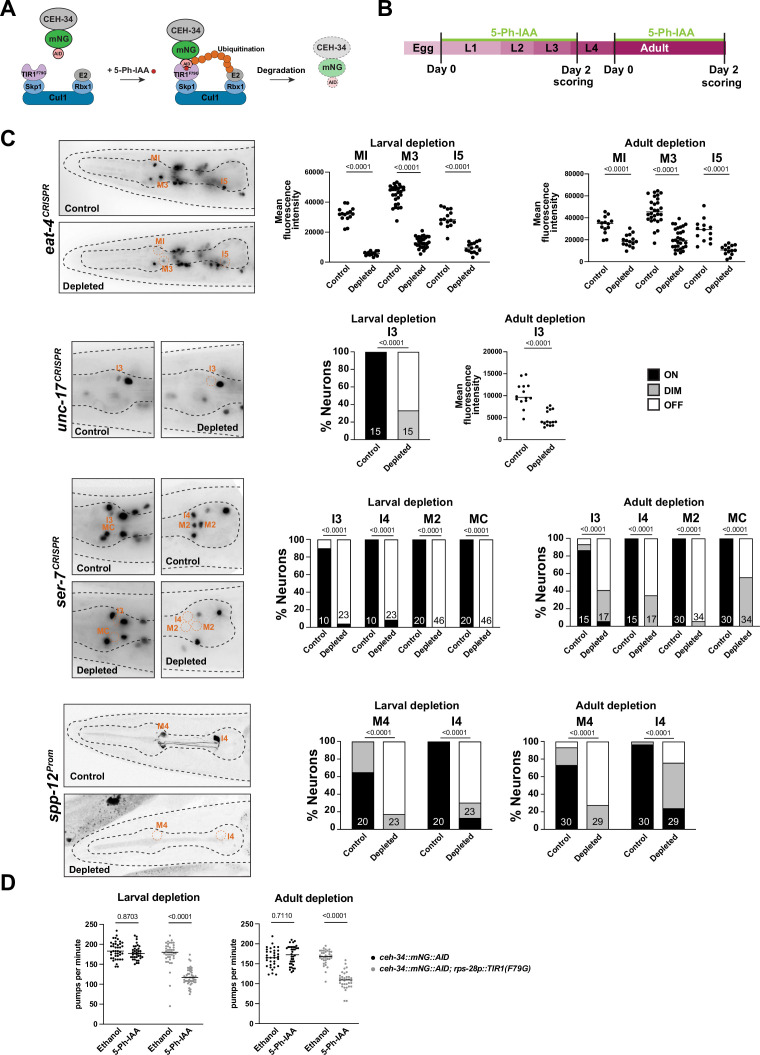
Figure 7. ceh-34 is continuously required to maintain gene expression and function of pharyngeal neurons.
(A) Schematic of the AIDv2 system (Hills-Muckey et al., 2022). Skp1, Cul1, Rbx1, and E2 are phylogenetically conserved components of the E3 ligase complex. TIR1F79G is a modified plant-specific substrate-recognizing subunit of the E3 ligase complex. In the presence of the auxin analog (5-Ph-IAA), the enzyme TIR1F79G binds to the AID fused to a protein of interest, leading to ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of the targeted protein. (B) Schematic depicting the 5-Ph-IAA treatment. Synchronized populations of worms at the L1 and young adult stage were transferred onto 5-Ph-IAA-coated plates and scored 48 hr later. Worms were expressing TIR1F79G ubiquitously under the rps-28 promoter (cshIs140). The ceh-34 locus was tagged with mNG::AID (ot903). (C) ceh-34 is required for maintained expression of identity genes. Reporter genes used are spp-12 (otIs868) and CRISPR/Cas-9-engineered reporter alleles for eat-4 (syb4257), unc-17 (syb4491), and ser-7 (syb4502). Since ceh-34::mNG::AID (ot903) and reporter genes scored are all fluorescent green, and this was obscuring the scoring on ethanol conditions, the control conditions are reporter genes on their own treated with 5-Ph-IAA. Representative pictures of larval depletion are shown on the left and quantification for larval and adult depletion is shown on the right. Quantification is only shown for neurons that were affected. Neurons unaffected by temporally controlled 5-Ph-IAA addition are also unaffected by constitute 5-Ph-IAA addition, indicating an inability to completely deplete CEH-34 protein. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired t-test, Fisher’s exact test, or chi-square test. N is indicated within each bar and represents number of neurons scored. (D) ceh-34 is required for maintained pharyngeal function. Larval and adult ceh-34 depletion results in decreased pharyngeal pumping. Statistical analysis was performed using two-way ANOVA.