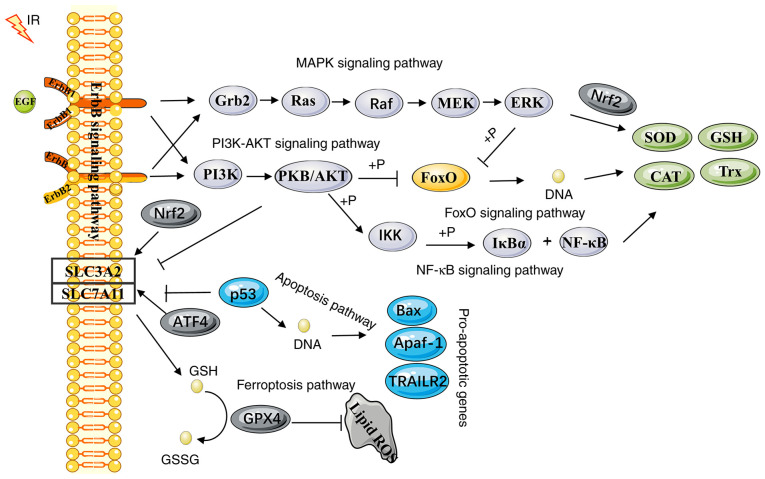
Figure 3.
Activation of oxidative stress-related pathways by radiotherapy. In response to IR, activated ErbB1 and ErbB2 (via interaction with one of the ligand-bound partners) induce the subsequent activation of downstream signaling pathways that include MAPK, PI3K/AKT and FoxO. The activation of the MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways increases the expression levels of Nrf2, thereby activating several antioxidant systems in response to oxidative stress. The FoxO-target genes include various genes encoding antioxidant proteins, which have a complex role in the induction of oxidative stress. It may not only activate the antioxidant system to promote tumor cell survival, but also promote apoptosis. NF-κB is another key pathway regulating the fine balance of the cellular redox status. The binding of the NF-κB proteins to DNA regulates the transcription of various potential antioxidant targets. In addition, IR activates the SLC7A11/GPX4 axis, which is considered to be one of the most important means of regulating oxidative stress via the ferroptotic pathway. IR, ionizing radiation; ErbB, Erb-b receptor tyrosine kinase; FoxO, forkhead box protein O; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; GPX4, glutathione reductase 4; SOD, superoxide dismutase; CAT, catalase; Trx, thioredoxin; Nrf2, nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2.