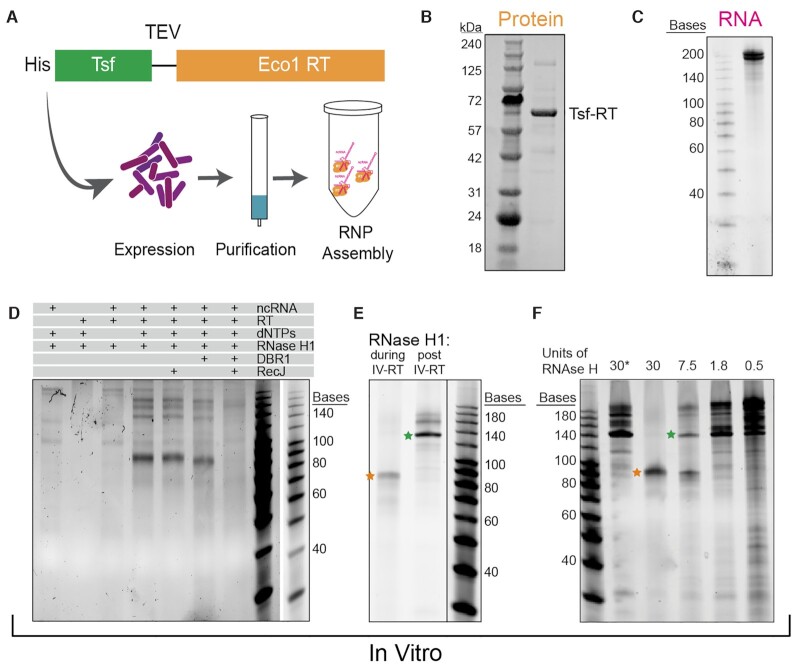
Figure 3.
In vitro validation of RNase H1 as a requirement for correct termination. (A) Schematic showing the purification of Eco1 RT (orange) with a His/Tsf tag on the N-terminus with a TEV linker. (B) SDS-PAGE gel of purified Retron-RT. (C) TBE-urea gel of in vitro transcribed RT-RNA. (D) In vitro production of RT-DNA. Components of the reaction are shown above. RT-DNA of ∼85 bases is produced in the presence of Eco1 ncRNA, RT, dNTPs and RNase H1. This RT-DNA is protected at the 5′ end against RecJ, debranched by DBR1, and degraded by RecJ after debranching. RNase A/T1 was added to all reactions before analysis on a TBE–urea gel. (E) Gel showing RT-DNA production when RNase H1 is present during the reaction vs. when it is added after the reaction has been quenched. Orange star represents the canonical length of Eco1 RT-DNA and the green star represents the RT-DNA product that does not terminate correctly. (F) RT-DNA production with a titration of RNase H1 present during the reaction. Asterisk indicates that RNase H1 was added after the reaction.