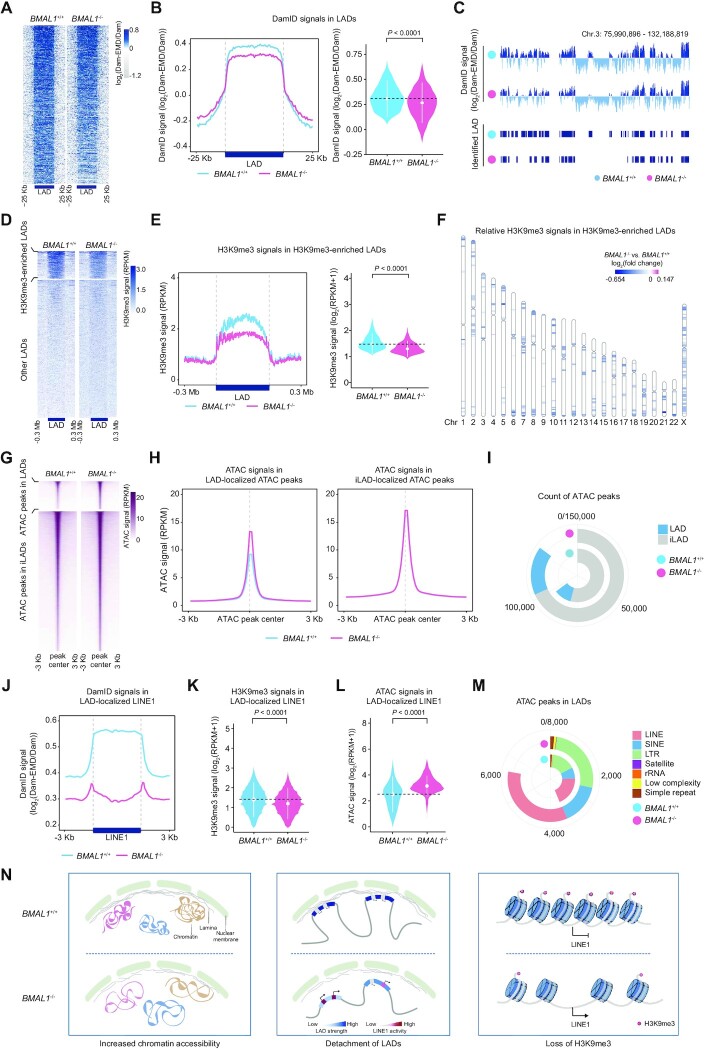
Figure 3.
(A) Heatmap showing the DamID signals (log2(Dam-EMD/Dam)) ranging from 25 kb upstream to 25 kb downstream of LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. The color key from gray to blue indicates low to high DamID signal. (B) DamID signals in LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. Left, metaplot showing the DamID signals (log2(Dam-EMD/Dam)) ranging from 25 kb upstream to 25 kb downstream of LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. Right, violin plot showing the DamID signals (log2(Dam-EMD/Dam)) in LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. The white dots represent the median values, and the white lines represent the interquartile range (IQR) from smallest to largest. Two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test. (C) Representative tracks of DamID signals and identified LAD regions in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. (D) Heatmap showing the H3K9me3 signals (RPKM) ranging from 0.3 Mb upstream to 0.3 Mb downstream of H3K9me3-enriched LADs (top panel) and other LADs (bottom panel) in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. The color key from white to blue indicates low to high H3K9me3 signal. (E) H3K9me3 signals in H3K9me3-enriched LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. Left, metaplot showing the H3K9me3 signals (RPKM) in H3K9me3-enriched LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. Right, violin plot showing the H3K9me3 signals (log2(RPKM + 1)) in H3K9me3-enriched LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. The white dots represent the median values, and the white lines represent the interquartile range (IQR) from smallest to largest. Two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test. (F) Chromosome ideogram showing the relative H3K9me3 signals in H3K9me3-enriched LADs across the 23 chromosomes of LP (P9) BMAL1–/– hMPCs compared to BMAL1+/+ hMPCs. The color key from blue to amaranth indicates low to high relative H3K9me3 level. (G) Heatmap showing the ATAC signals (RPKM) ranging from 3 kb upstream to 3 kb downstream of LAD-localized ATAC peak centers (top panel) and iLAD-localized ATAC peak centers (bottom panel) in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. The color key from white to amaranth indicates low to high chromatin accessibility. (H) Metaplot showing the ATAC signals (RPKM) ranging from 3 kb upstream to 3 kb downstream of LAD-localized ATAC peak centers (left panel) and iLAD-localized ATAC peak centers (right panel) in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. (I) Ring plot showing the count of ATAC peaks in LADs and iLADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. (J) Metaplot showing the DamID signals (log2(Dam-EMD/Dam)) ranging from 3 kb upstream to 3 kb downstream of LAD-localized LINE1 regions in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. (K) Violin plot showing the H3K9me3 signals (log2(RPKM + 1)) in LINE1s localized in H3K9me3-enriched LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. The white dots represent the median values, and the white lines represent the interquartile range (IQR) from smallest to largest. Two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test. (L) Violin plot showing the ATAC signals (log2(RPKM + 1)) for ATAC peaks in LAD-localized LINE1 regions in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. The white dots represent the median values, and the white lines represent the interquartile range (IQR) from smallest to largest. Two-sided Wilcoxon signed-rank test. (M) Ring plot showing the count of ATAC peaks in indicated repetitive elements in LADs in LP (P9) BMAL1+/+ and BMAL1–/– hMPCs. (N) Diagrams summarizing epigenomic alterations in BMAL1–/– hMPCs detected by DamID-seq, H3K9me3 ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq.