Figure 5.
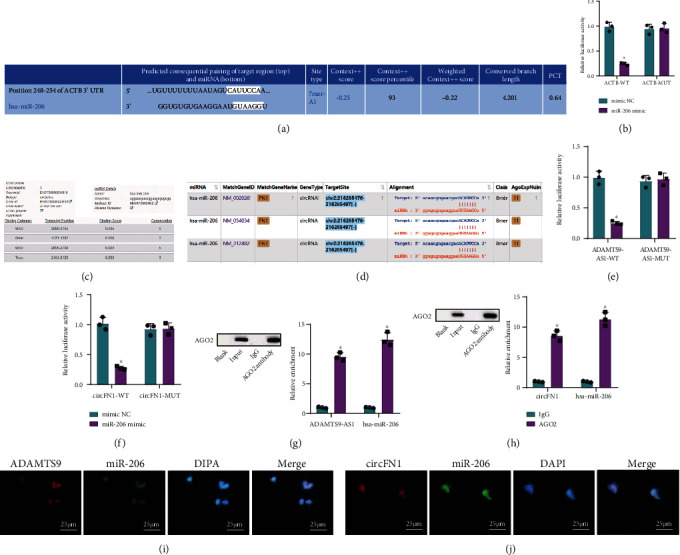
The targeted regulatory relationships between ADAMTS9-AS1/miR-206/ACTB and circFN1/miR-206/ACTB pathways. (a) Schematic diagram of the binding sites of miR-206 and ACTB predicted on the TargetScan website. (b) The results for miR-206 and ACTB verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. (c) The binding sites of ADAMTS9-AS1 and miR-206 predicted using the DIANA-LncBase database. (d) The binding sites of circFN1 and miR-206 predicted using the Starbase database. (e) The results of ADAMTS9-AS1 and miR-206 verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. (f) The results of circFN1 and miR-206 verified by dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. (g) Results of ADAMTS9-AS1 and miR-206 verified by RIP assay. (h) Results of circFN1 and miR-206 verified by RIP assay. (i) Results of ADAMTS9-AS1 and miR-206 observed by FISH. (j) Results of circFN1 and miR-206 observed by FISH. Measurement data were expressed by mean ± standard deviation. Independent sample t test was conducted for comparisons between two groups. ∗P < 0.05 vs. the mimic NC group or the IgG group.
