Figure 2: Neuroinflammation increases leukocyte binding to cpLECs.
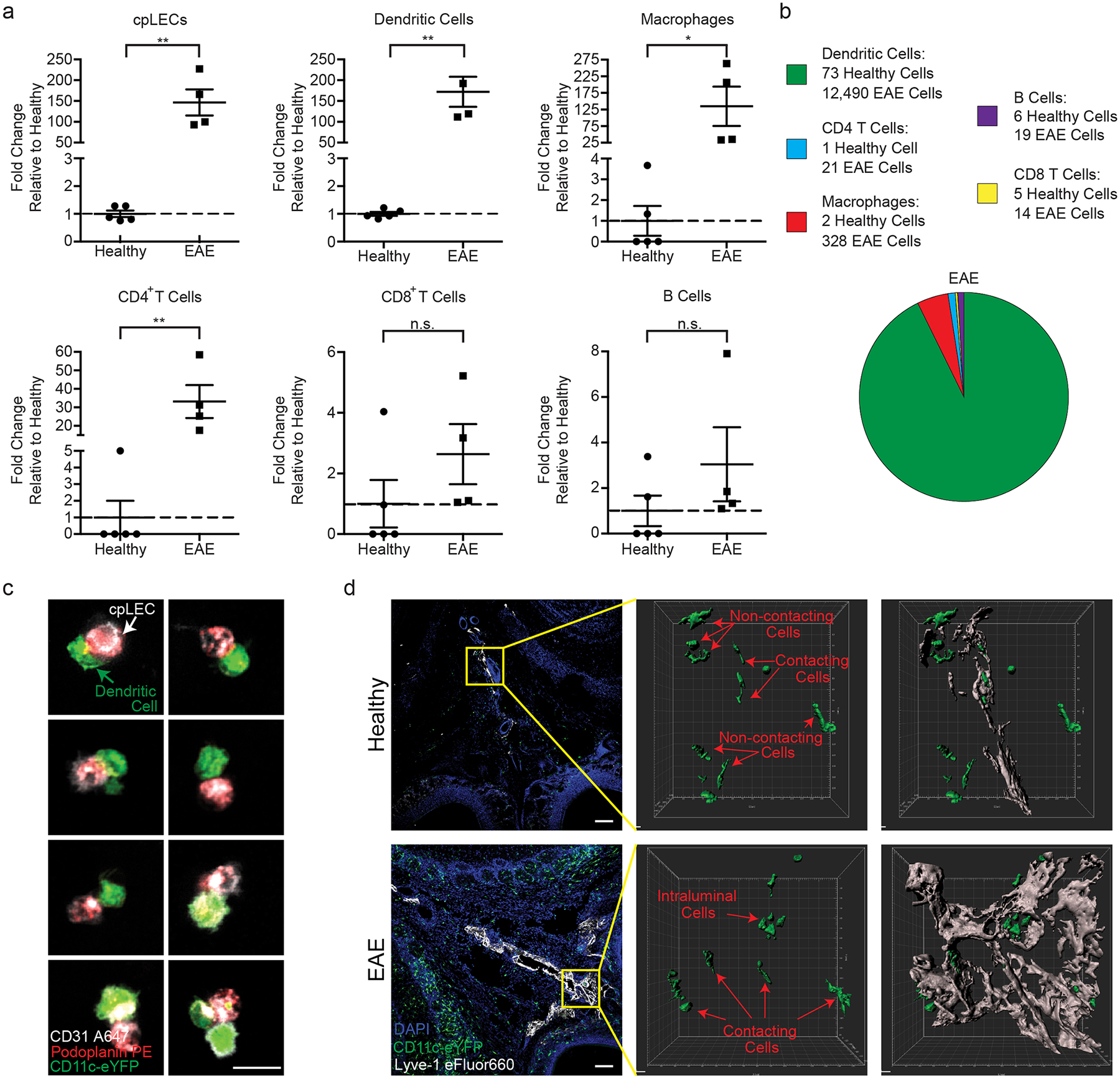
(a): Quantitation of the average fold changes in cpLECs, dendritic cells, macrophages, CD4 and CD8 T cells, and B cell numbers during EAE score 3.0 relative to healthy. n = 5 healthy mice, 4 EAE mice; data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean. cpLECs, p = 0.0012; dendritic cells, p = 0.0010; macrophages, p = 0.0367, CD4 T cells, p = 0.0047, CD8 T cells, p = 0.2300, B cells, p = 0.2474; unpaired Student’s t-test.
(b): Pie charts showing the relative composition of different leukocytes bound to cpLECs in healthy controls and EAE mice. 12,872 cells total.
(c): CD11c-eYFP transgenic reporter mice were induced with EAE and underwent the same harvest protocol as (a – b) to visualize leukocyte – LEC binding using confocal microscopy on day 15 post-immunization at score 3.0. Representative confocal microscopy images show doublets and the occasional triplet consisting primarily of a CD11c+ dendritic cell bound to a CD31+ Podoplanin+ LEC. Scale bar = 10 μm
(d): CD11c-eYFP transgenic reporter mice were induced for EAE, and dendritic cell – LEC interactions were visualized in situ using immunohistochemistry and 3D rendering with IMARIS. The top panel is representative of healthy, and the bottom panel is representative of EAE animals at score 3.0, 15 days post-immunization. Scale bar = 100 μm
