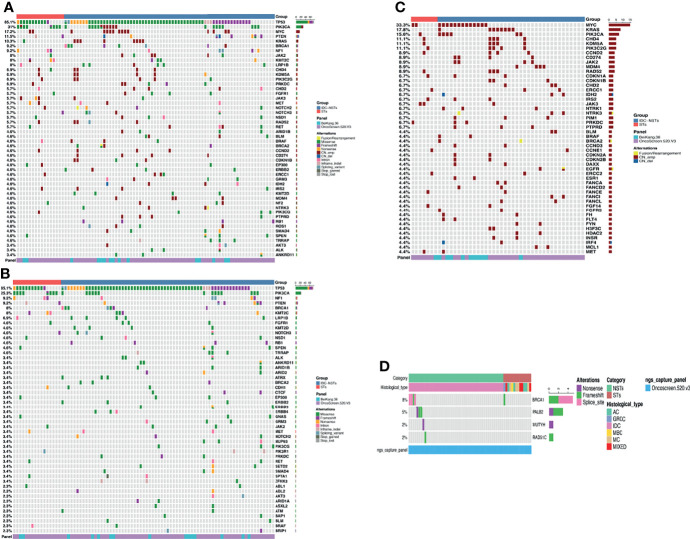
Figure 2.
The landscape of genetic alterations in TNBC. Top 50 genomic alterations are shown in the Oncoprint. Different colors denote different types of alterations and different clinicopathologic features. (A) Summary of the features of the genomic alteration of the 89 patients with TNBC. Tumor samples were grouped according to histologic types as: no-special type (NSTs, n = 72) and special type (STs, n = 17). The top bar shows the histologic type of each patient; the side bar (rows) summarizes the percentage of tumors with alterations in each gene (left) and alteration composition for each gene in the entire cohort (right). (B) Summary of the features of the genomic mutation of the 89 patients with TNBC. Tumor samples were grouped according to histologic types as: no-special type (NSTs, n = 72) and special type (STs, n = 17). The top bar shows the histologic type of each patient; the side bar (rows) summarizes the percentage of tumors with mutations in each gene (left), and the mutation composition for each gene in the entire cohort (right). (C) Summary of copy number variations and Fusion in the 45 patients with TNBC who carry copy number variations. Tumor samples were grouped according to histologic types as: no-special type (NSTs, n = 38) and special type (STs, n = 7). The top bar shows each patient’s histologic type; the side bar (rows) summarizes the percentage of tumors with variation in each gene (left) and alteration composition for each gene (right), in the entire cohort. (D) Summary of germline mutation of the 62 patients with TNBC. Tumor samples were grouped according to histologic types as: no-special type (NSTs, n = 48) and special type (STs, n = 14). The side bar (rows) summarizes the percentage of tumors with mutation in each gene (left) and alteration composition for each gene (right), in the entire cohort. TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; NST, no-special type; ST, special type; indel, insertions or deletions; LGR, large genomic rearrangement; CN_amp, copy number amplification; CN_del, copy number deletion.