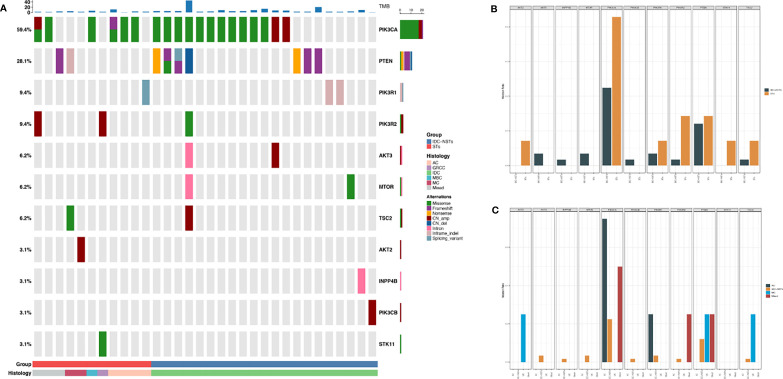
Figure 5.
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis reveals distinct pathways in NSTs and STs tumors of TNBC. In total, 36.2% of the NSTs patients and 78.6% of the STs patients had at least one clinically relevant genomic alteration in genes involved in the PI3K-AKT signaling pathways, respectively. (A) Summary of the features of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathways genomic alteration of the 32 patients with TNBC. Tumor samples were grouped according to histologic types as: no-special type (IDC-NSTs, n=21) and special type (STs, n=11). (B) Comparison of the features of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathways genomic alteration between NSTs and STs TNBC patients. (C) Comparison of the features of the PI3K-AKT signaling pathways genomic alteration among STs TNBC patients. TNBC, triple-negative breast cancer; NST, no-special type; ST, special type; TMB, tumor mutation burden.