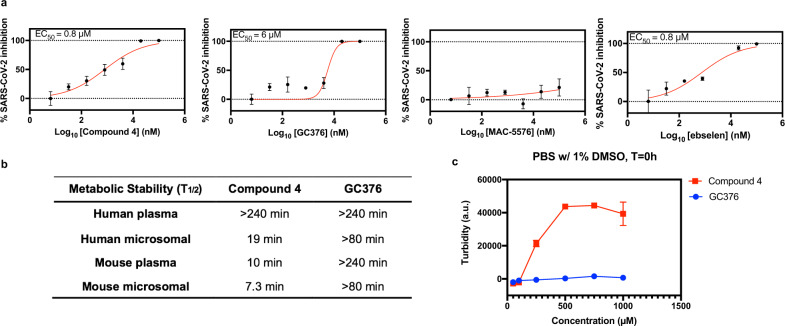
Fig. 2. Evaluation of lead compounds for cellular antiviral potency, metabolic stability, and solubility.
a Ability of compound 4, GC376, MAC-5576, and ebselen to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 viral infection in cell culture. Stocks of SARS-CoV-2 strain 2019-nCoV/USA_WA1/2020 were propagated and titered in Vero-E6 cells. Serial dilutions of the test compound were prepared in cell media (EMEM + 10% FCS + penicillin/streptomycin), overlaid onto cells, and then virus was added to each well at an MOI (multiplicity of infection) of 0.2. Cells were incubated at 37 °C under 5% CO2 for 72 h before viral RNA extraction from the supernatant and quantification against a RNA standard by quantitative reverse-transcriptase PCR (qRT-PCR). Data are plotted as the mean ± s.d., n = 3 biological replicates. b Half-life of compound 4 and GC376 in human and mouse (CD-1) plasma and liver microsomes (with NADPH). c Solubility test (light scattering) of compound 4 and GC376 in PBS with 1% DMSO. Data are plotted as the mean ± s.d., n = 3 biological replicates. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.