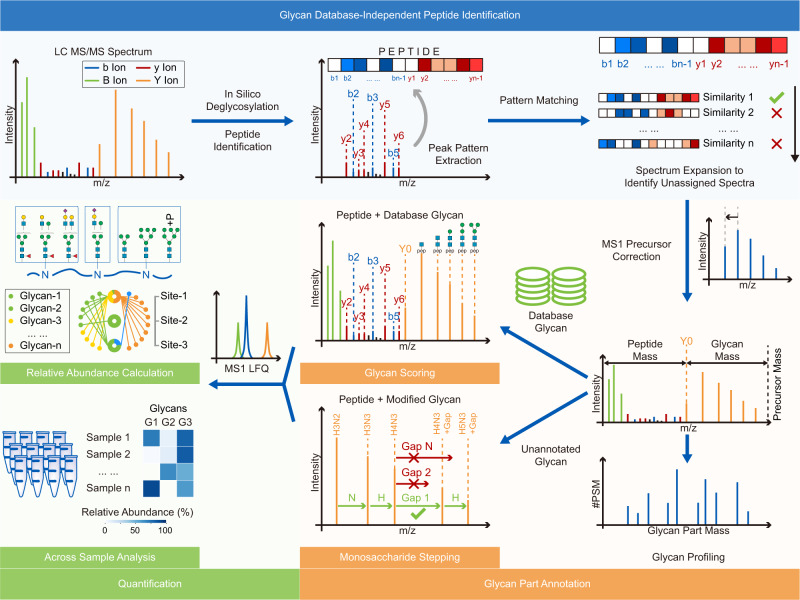
Fig. 1. Workflow of Glyco-Decipher.
Glyco-Decipher contains three modules: (1) Glycan database-independent peptide matching. The in silico deglycosylated spectra are searched against the protein database without setting any glycans as modifications, which determines the peptide backbone for glycopeptide spectra with rich peptide fragment ions. Then, the fragmentation patterns of the peptide backbones are extracted and utilized to match spectra that remain unannotated. This step, termed “spectrum expansion”, enables the identification of peptide backbones of glycopeptide spectra with poor peptide fragmentation. (2) Glycan annotation. The mass of the glycan part is precisely derived by the mass difference between the precursor and the peptide backbone. The mass profile of glycans in a system is constructed without the use of glycan databases. For glycan annotation, the experimental B/Y ions in glycopeptide spectra are first matched to their theoretical fragment ions of database glycans to identify glycans. For glycans that do not match any database entries, Glyco-Decipher performs monosaccharide stepping to reveal the composition of modified glycans and potential modification moiety on them. (3) Quantification. The quantification module based on the elution profiles of glycopeptides is embedded in Glyco-Decipher and allows the computation of the abundance distributions of site-specific glycans.