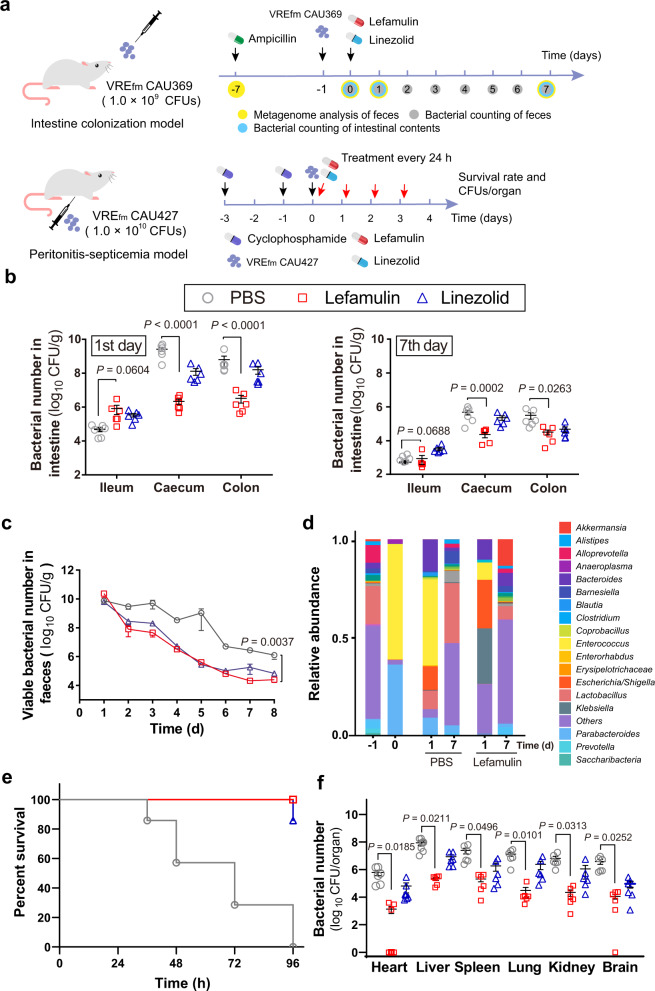
Fig. 5. Efficacy of lefamulin against VREfm in vivo.
a Scheme of mouse intestinal colonization model and VREfm peritonitis-septicemia model. b Bacterial loads in the ileum, cecum and colon. Mice (n = 6 per group) were given 1 × 109 CFUs of VREfm CAU369, under the treatment of a single dose of 5 mg/kg lefamulin or linezolid. c Bacterial loads in feces. Mice (n = 6 per group) were given 1 × 109 CFUs of VREfm CAU369 by oral gavage, with administration of 5 mg/kg lefamulin or linezolid. d Fecal microbiota was profiled of mice infected with VREfm CAU369 in the presence of 5 mg/kg lefamulin at different points using 16S rRNA gene sequencing. e Survival rates of peritonitis-septicemia mice infected with VREfm CAU427 (1.0 × 1010 CFUs) in the presence of lefamulin (10 mg/kg). f Lefamulin decreased bacterial loads in different organs in the mouse peritonitis-septicemia model (n = 6 per group). Data in b, c and d were presented as mean values ± S.D, f was presented as mean values ± SEM. P-values in b, c and d were determined by non-parametric one-way ANOVA and in f was determined by two-tailed t-test.