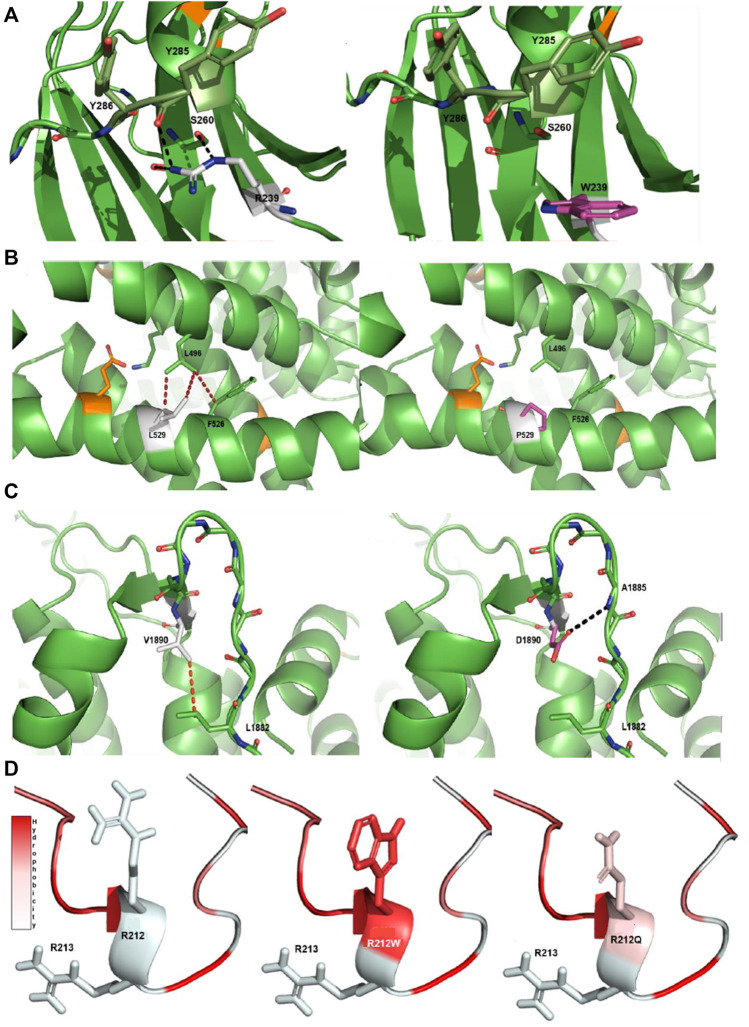
FIGURE 2.
Protein modeling of variants with a notable effect on protein structure. (A) R239W VUS-high in PKCγ protein. The native R239 interacts with S260 and Y285 through a hydrogen bonding network. The aromatic side chain of the mutant W is unable to establish an interaction network in the same manner as the native arginine. (B) L529P VUS-high in Cav2.1 protein. The native L529 engages in a network of hydrophobic interactions with L496 and F526. The introduction of P in the middle of the helix introduces a steric clash with these hydrophobic residues and is detrimental for helix stability (Visiers et al., 2000). (C) V1890D VUS-high in Cav2.1 protein. The native V1890 interacts with L1882 through a hydrophobic interaction. The mutated D changes the conformation of the backbone of the protein, disturbing the β-sheet structure and forming a new hydrogen bond with the main chain of A1885. Native side chains are shown as white, mutated side chains as pink, known pathogenic mutations as orange, hydrophobic interactions as red dashes and hydrogen bonds as black dashes. (D) R212Q VUS-semi high in pdyn protein. The R212Q mutation has similar hydrophobic properties to the known R212W, which is known to decrease the cleavage efficiency of dynorphin, and likely functions in a similar manner. Arginine (R), tryptophan (W), serine (S), tyrosine (Y), valine (V), aspartic acid (D), leucine (L), proline (P), glutamine (Q) and phenylalanine (F).