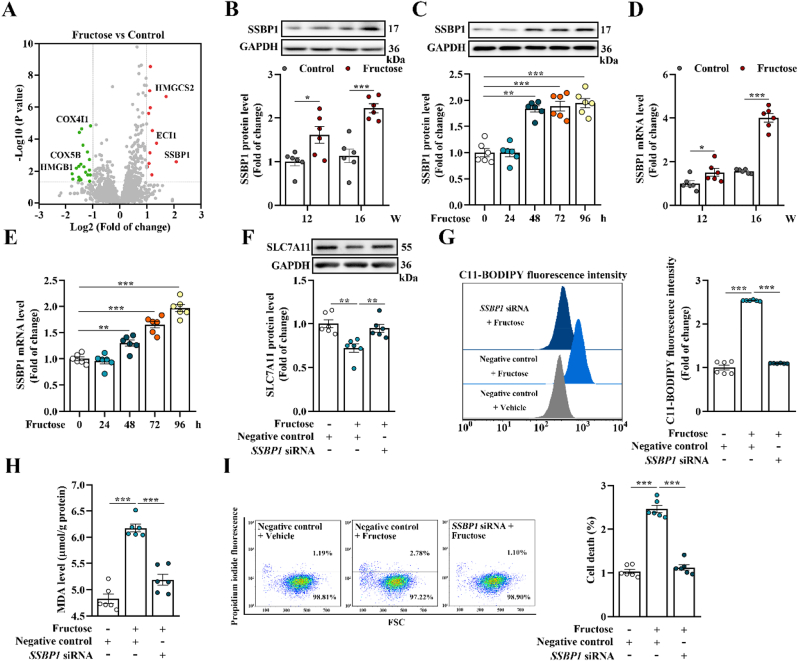
Fig. 2.
SSBP1 triggers podocyte ferroptosis in high fructose-induced glomerular injury. (A) Dysregulated proteins in high fructose-stimulated rat glomeruli at 16th week were identified by iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis. Differences were considered statistically significant when fold change >2 (red) or < 0.5 (green) and P < 0.05. (B–C) Western blot analysis of the protein level of SSBP1 in high fructose-stimulated rat glomeruli and podocytes (n = 6 per group). (D–E) The mRNA level of SSBP1 was measured by qPCR in high fructose-exposed rat glomeruli and podocytes (n = 6 per group). (F–I) Podocytes were transfected with SSBP1 siRNA as well as negative control and then cultured with vehicle or fructose (5 mM). Western blot analysis of the protein level of SLC7A11 in podocytes (n = 6 per group). Lipid peroxidation in podocytes was analyzed by C11-BODIPY (581/591) staining and measured by flow cytometer (n = 6 per group). The MDA level was measured by assay kit in podocytes (n = 6 per group). Podocyte death was analyzed by propidium iodide staining and measured by flow cytometer (n = 6 per group). Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. P-values were acquired by one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.