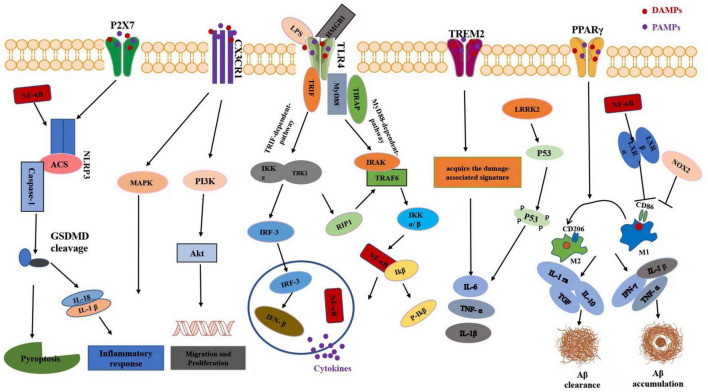
FIGURE 2.
Schematic diagram of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation signaling pathways after TBI. In response to TBI, DAMPs such as HMGB1 can promote priming of the NLRP3 inflammasome through NF-κB signaling. In microglia, activation of P2X7 receptor could stimulate the NLRP3 inflammasome, which subsequently leads to the outflow of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-18 and IL-1β. CX3CL1 is also known to induce microglia activation through intracellular phosphorylation of microglial p38 MAPK. Further, treatment of cultured microglia with CX3CL1 promoted cell survival and inhibited Fas ligand-induced cell death via the Akt signaling pathway. TLR signaling initiates acute inflammatory response by promoting the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Ligand binding to TLR4 activates either a MyD88-dependent NF-κB activation or MyD88-independent activation of interferon regulatory factor-3 (IRF-3) activation and the subsequent expression of IFNβ. The TREM2 pathway is responsible for switching from a homeostatic to a neurodegenerative microglial phenotype after phagocytosis of apoptotic neurons. Upon activation, the PPARs regulate inflammation via trans-reexpression of multiple inflammatory signaling systems such as NFκB, activator protein-1 (AP-1), signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) to result in M1/M2 microglia polarization and facilitate it toward an anti-inflammatory state. In LPS induced neuroinflammation, LRRK2 could phosphorylate p53 and promote the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α. Activation of NOX2 aggravated inflammatory-mediated neurodegeneration after TBI via inhibiting switch from M1-like activation to M2- like activation of microglia. Pro-inflammatory cytokines expressed by microglia, including interferon-γ, interleukin-1β, and tumor necrosis factor-α, can specifically stimulate Aβ accumulation while anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1ra, IL-10, and TGF preclude formation of Aβ. HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; N-FκB, nuclear factor-kappa B; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; IFN-β, IRF-3-inducing interferon-b. TREM2, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2. LRRK2, leucine-rich repeat kinase 2; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. IL-1ra, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist; Aβ, beta amyloid.