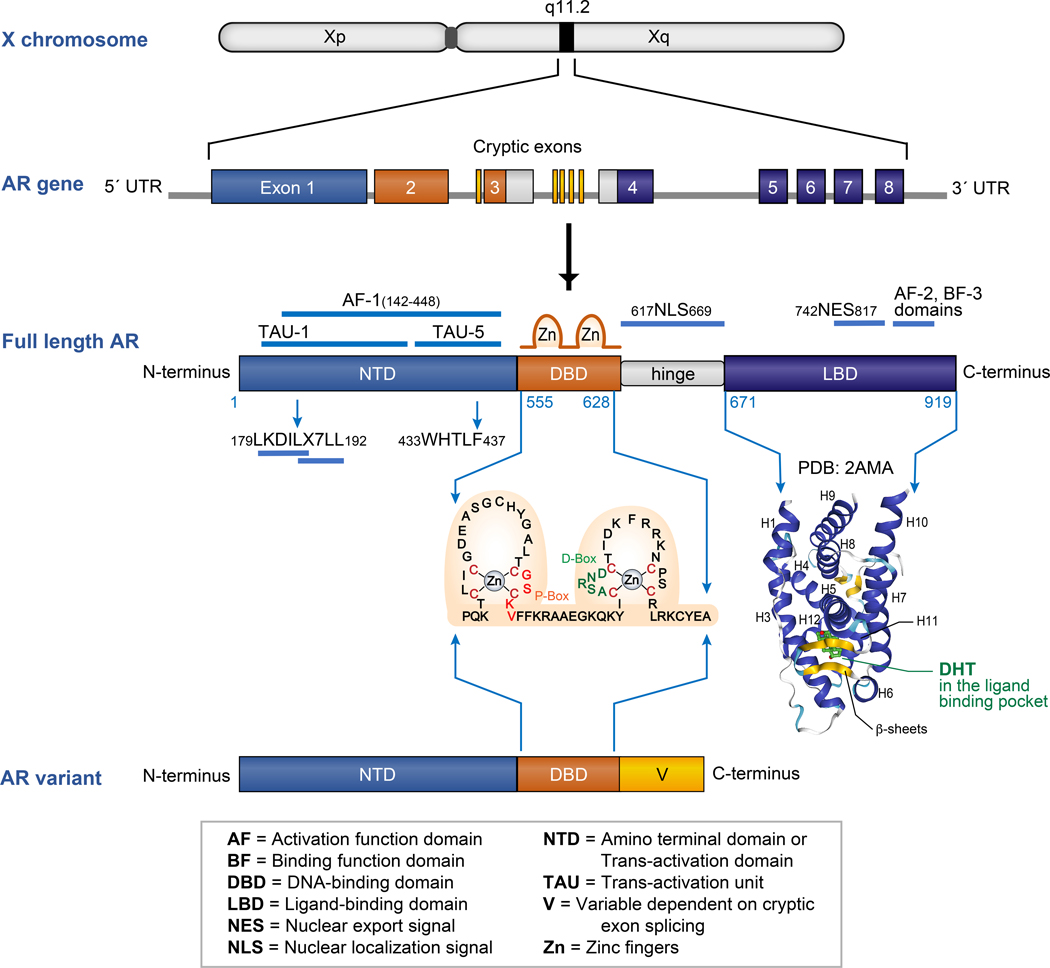
Figure 1:
AR gene and protein structure: AR is located on the X chromosome at position q11.2. The AR gene is encoded by 8 exons that are color coded to represent the domains of the full-length AR protein they encode. The full-length AR is comprised of an amino terminal domain (NTD, in blue), DNA binding domain (DBD, in orange), a short hinge region (in grey) and a ligand binding domain (LBD, in purple). The amino acid sequence of the two zinc finger units containing the P-box and D-box of the AR DBD are shown. The structure of human AR LBD domain with a DHT bound in its ligand binding pocket is represented (PDB: 2AMA). AR variants contain the AR NTD and DBD but lack the LBD. The C-termini of AR variants have variable lengths (V, in yellow) and sequences based on the splicing of the cryptic exons in the AR gene.