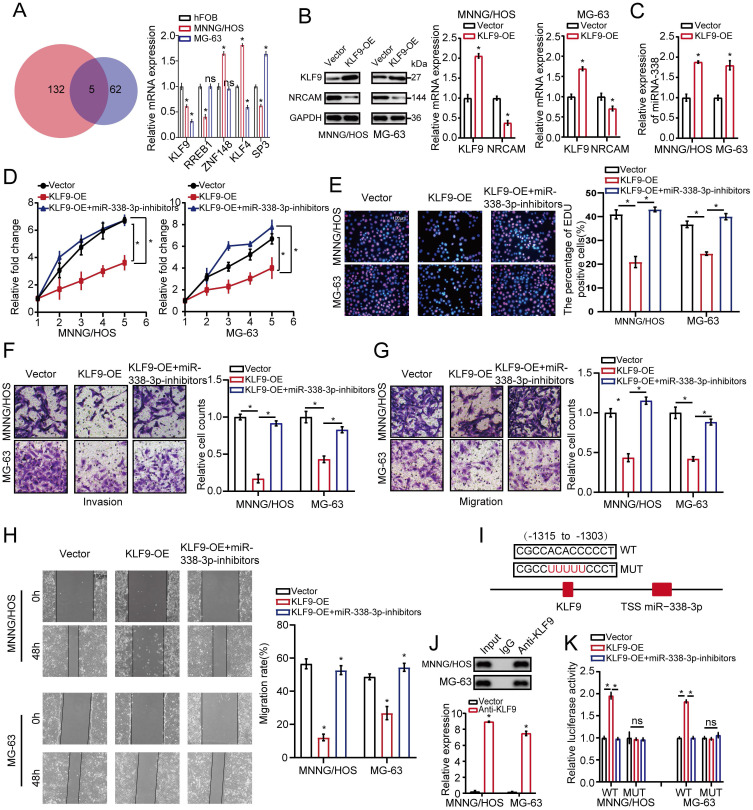
Figure 5.
KLF9 targets miR-338-3p directly in osteosarcoma cells. (A) qRT-PCR assay was used to assess the expression of the five candidate TFs screened by overlapping DEGs (137) with predicted targets (67). (B) The role of elevated KLF9 expression in NRCAM in osteosarcoma cells was explored by applying western blot assay. (C) The function of raised KLF9 expression on miR-338-3p expression in osteosarcoma cells was investigated by employing qRT-PCR analysis. (D, E) Elevated KLF9 expression could suppress the proliferation of osteosarcoma cells, and the effect may be reversed via diminished miR-338-3p expression. Scale bars = 100μm. (F, G, H) Raised KLF9 expression could significantly inhibit migration and invasion of osteosarcoma cells, which could be rescued by miR-338-3p decline. Scale bars = 100μm. (I) A schematic exhibited the proximal region of the miR-338-3p promoter that was targeted by KLF9. (J) ChIP assay was adopted to validate the binding correlation between KLF9 and the miR-338-3p promoter in osteosarcoma cells. (K) Luciferase activity was increased in the WT miR-338-3p promoter with KLF9 elevation that was clearly rescued via miR-338-3p diminishment. No significant change was unveiled in luciferase activity when KLF9 targeting sites at -1315 to -1303bp were mutated. Data was presented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. *, P <0.05; ns, not significant.