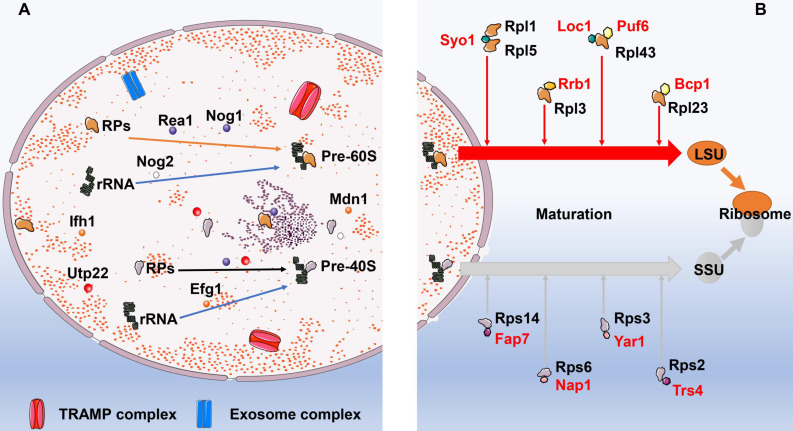
Figure 2.
The biogenesis and maturation of ribosomes. A: The biogenesis of ribosomes. In the nucleolus, ribosomal proteins firstly are combined with pre-ribosome RNAs (pre-rRNA) to form pre-60S and pre-40S. This process is regulated by multiple molecules and dedicated chaperones. These essential biogenesis factors include Ifh1, Utp22, U3-snoRNP, UTP-A, UTP-B, and UTP-C. In addition to above mentioned molecules, a number of complexes are manifested to play roles in the surveillance and turnover of misassembled preribosomes as well, such as the TRAMP complex and exosome complex of exonucleases. B: The maturation of ribosomes. Following synthesis of ribosomal subunit precursors in the nucleus, they need to enter the cytoplasm via the nuclear pore prior to combining with RPs to complete the maturation process. Dedicated chaperones specifically transport RPs to ensure the successful implementation of this process. The dedicated chaperones in the biogenesis of 60S LSU include Rrb1, Sqt1, Acl4, and Bcp1. While the dedicated chaperones Fap7, Nap1, Yar1, and Trs4 are involved in the maturation of 40S SSU. Abbreviation: Ifh1: interacts with forkhead 1; Utp22: U3 small nucleolar RNA-associated protein 22; UTP: U3 small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein particles; TRAMP: TRf4/5-Air1/2-Mtr4 polyadenylation; RPs: ribosomal proteins; LSU: the 60S large subunit; SSU: the 40S small subunit.