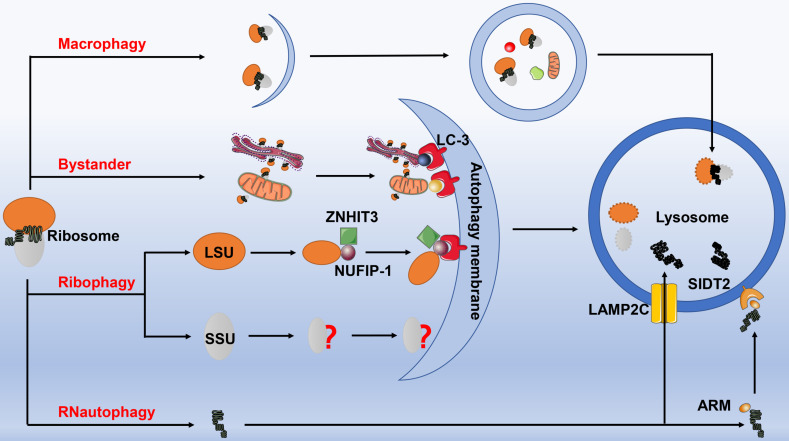
Figure 5.
The autophagy of ribosomes. Ribosomes can be degraded by four autophagic pathways. 1) Macrophagy. Ribosomes are non-selectively wrapped by autophagosomes, and then fused with lysosomes to form autophagic lysosomes for degradation. 2) Ribophagy. The ribophagy receptor NUFIP-1 specifically recognizes the large ribosomal subunits under the help of ZNHIT3, and then binds to the LC-3B on the autophagosome membrane to complete the next process, however, the precise mechanism for degrading small ribosomal subunit remains to be elucidated. 3) Bystander autophagy pathway. When other selectively organelle autophagy occurs, such as mitochondrial autophagy, endoplasmic reticulum autophagy, etc., ribosomes can be engulfed and degraded incidentally. 4) RNautophagy. rRNA directly enters the lysosome for degradation through the protein receptor LAMP2C and SIDT2 (with the assistance of ARM) on the lysosomal membrane. Abbreviation: NUFIP-1: nuclear fragile X mental retardation-interacting protein 1; ZNHIT3: Zinc finger HIT domain containing protein 3; LAMP2C: lysosomal associated membrane protein 2C; SIDT2: SID-1 transmembrane family member 2; ARM: arginine-rich motif.