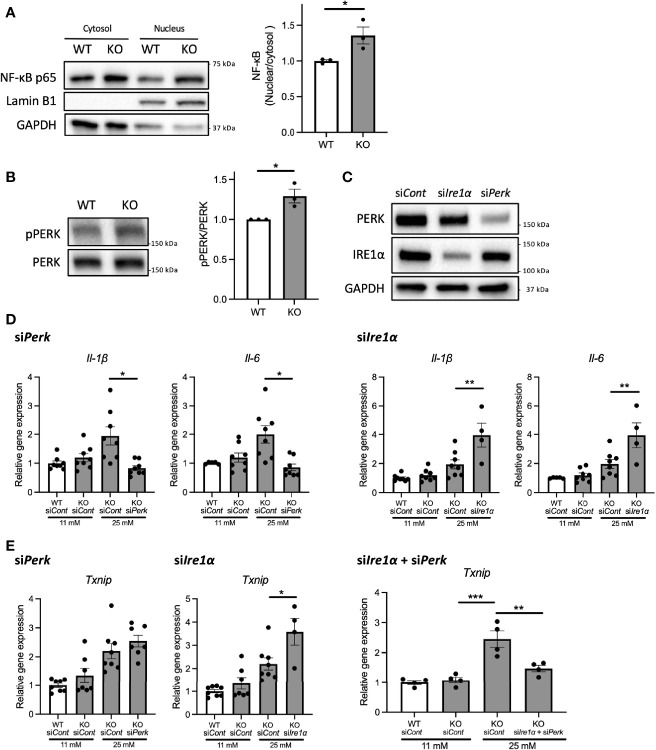
Figure 4.
PERK pathway regulates the high-glucose induced pro-inflammatory gene expression in Wfs1-deficient pancreatic β-cells. (A) Left panel: Immunoblot images of NF-κB p-65 in the cytosolic or nuclear fraction of Wfs1 wild-type (WT) and knockout (KO) INS-1 832/13 cells. WT and KO INS-1 832/13 cells were treated with 5 mM glucose for 18 h and then with 25 mM glucose for 30 min. Right panel: The ratio of nuclear and cytosolic NF-κB p-65 protein levels (n=3). (B) Left panel: Immunoblot images of pPERK and PERK. WT and KO INS-1 832/13 cells were treated with 5 mM for 16 h and then with 25 mM glucose for 24 h. Right panel: pPERK band intensity was quantified and normalized to total PERK (n=3). (C) Immunoblot images of PERK and IRE1α in WT and KO INS-1 832/13 cells treated with siRNA against Perk or Ire1α. (D) mRNA expression level of Il-1β and Il-6 normalized to 18srRNA in WT or KO INS-1 832/13 cells treated with 11 mM or 25 mM glucose for 30 h together with siRNA against Perk or Ire1α (n=4-8) (E) mRNA expression levels of Txnip normalized to 18srRNA in WT and KO INS-1 832/13 cells treated with 11 mM or 25 mM glucose for 6 h together with siRNA against Ire1α and Perk (n=4). Data are shown in mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.001.