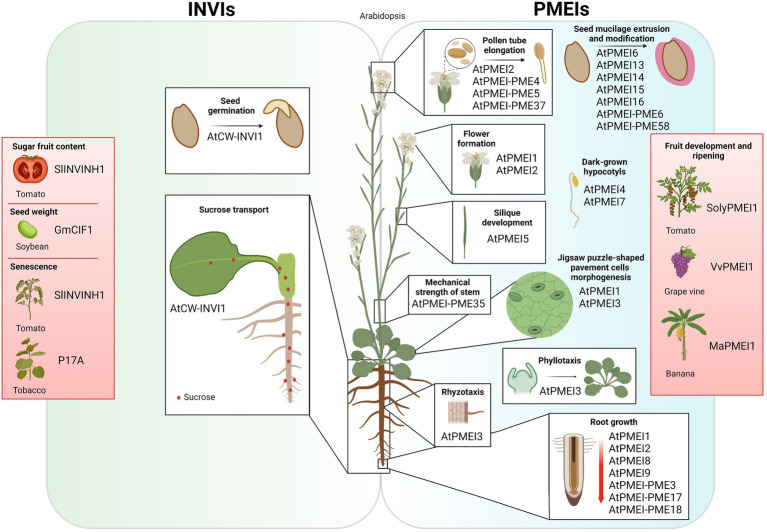
Figure 5.
Overview of INVIs and PMEIs functions in plant growth and development. INVIs control seed germination, sugar transport in roots; senescence and sugar fruit content. PMEIs play multiple roles in several physiological processes, such as pollen tube elongation, seed mucilage extrusion, and modification, flowering transition, silique development, mechanical strength of stem, phyllotaxis, rhyzotaxis, pavement cells morphogenesis, hypocotyl growth in the dark, and root growth, and they are also involved in fruit development and ripening.