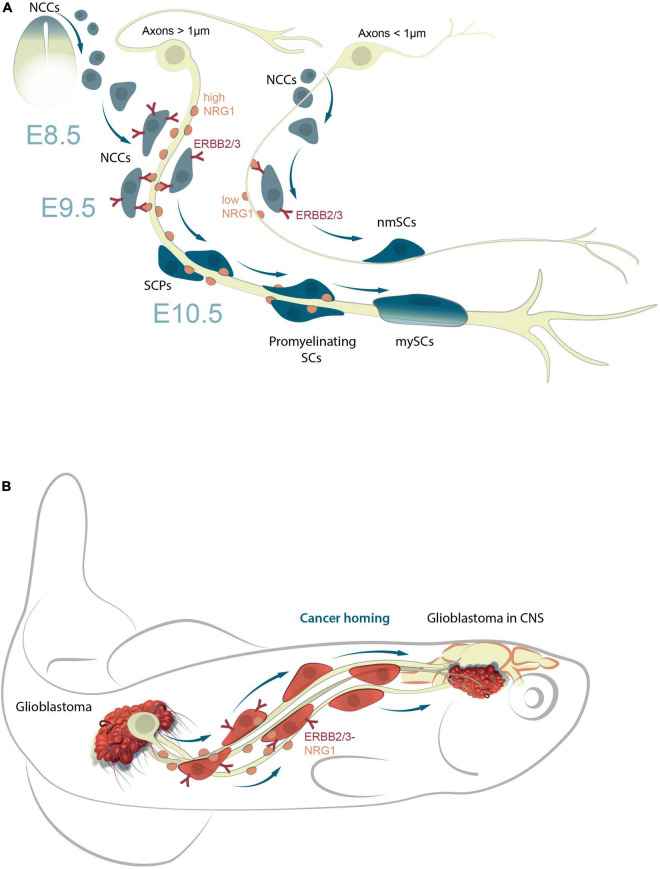
FIGURE 2.
NRG1-ERBB2/3 signal pathway responsible for the maturation of SCPs into mnSCs during development and in cancer homing. (A) NRG1-ERBB2/3 interactions are essential for cellular attachment to axons and migration of SCPs along peripheral nerves; SCP survival is dependent on NRG1 concentrations. Those that receive insufficient NRG1 signals undergo apoptosis, or remain NCCs. Those that receive sufficient NRG1 signals differentiate into iSCs and then mySC, or detach from axons on reaching target-tissues and differentiate into other cell types (neurons, chromaffin cells, odontoblasts, or pigment cells). (B) A model of NRG1-ERBB2/3 signaling in cancer homing from periphery to CNS (zebrafish model system). NRG1 and ERBB induce the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in certain cancers (e.g., breast) by modulating expression of proteins involved in invasion and metastasis. Eventually, the cancer-axonal molecular machinery triggers cancer cell dissemination and homing (e.g., glioblastoma migration from periphery to CNS) via nerve signals.