FIGURE 2.
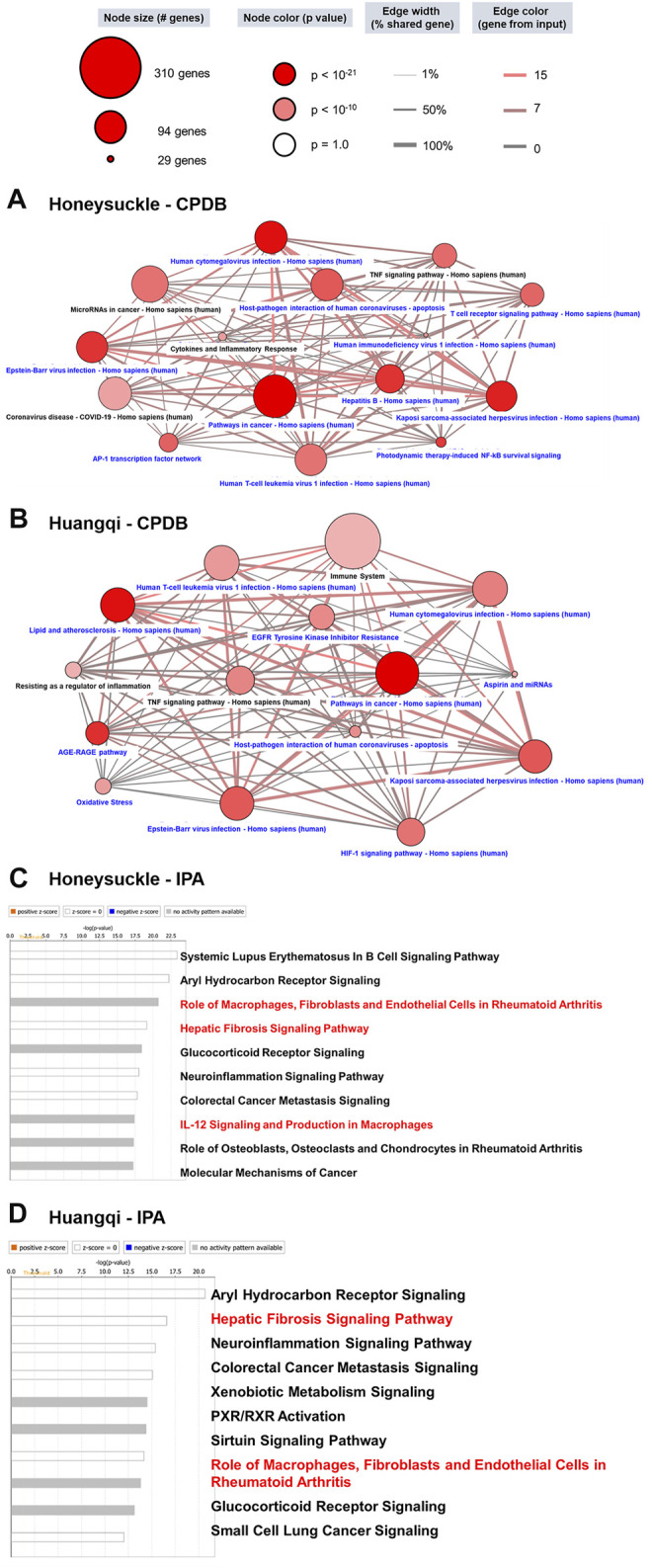
The potential mechanism of Honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica) and Huangqi (Astragalus membranaceus) via the bioinformatics workflow. (A) According to the results of the FDR-BH statistical analysis, we selected 66 significant honeysuckle targets to perform enrichment analysis via CPDB. To begin, 15 pathways were selected from the top 150 pathways (ranked by p-value < 0.001) using the following keywords: virus, viral, infection, microRNA (miRNA), immune, inflammation, TNF, interleukin (IL), interferon (IFN), cytokine, etc. Those pathways highlighted in black were focused upon to discuss the possible therapeutic potential of TCMs. The 15 selected pathways in this study were illustrated in the context of a network. The dot color denotes statistical significance where the darker color demonstrates a higher significance level. The dot size indicates the number of genes in the pathway, while the edge between two dots showed the relationship. (B) The 64 target genes of Huangqi were analyzed though the same process in CPDB. The bar chart shows the results of the IPA analysis of honeysuckle (C) and Huangqi (D). Since the target genes in this study were retrieved from a database or PubMed, there were no up- or down-regulated expression data. Thus, we predicted the potential pathway without up- or down-regulation. A white bar color (no activation change) or gray (unknown activation) was the degree of correlation with the input gene set. The pathways of interest in this study were highlighted red.
