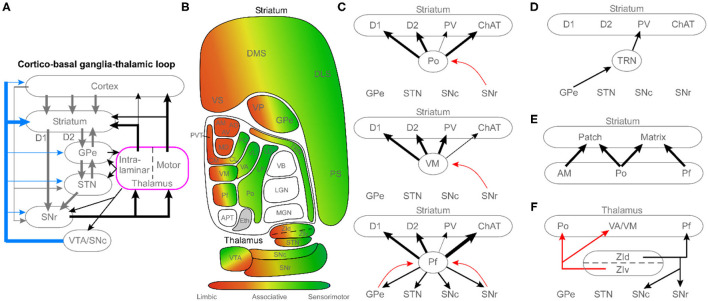
Figure 1.
Circuit diagrams illustrating the complex diversity of thalamic connections with the basal ganglia. (A) Schematic of the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamic loop, highlighting the central role of the thalamus as a major recipient of basal ganglia output, and an important source of basal ganglia inputs. (B) Diagram of the topographic organization of the thalamus and basal ganglia, organized by limbic, associative, and sensorimotor regions. (C) Circuit diagrams illustrating differences among higher-order thalamic nuclei, motor thalamus, and caudal intralaminar thalamic nuclei. Diagrams feature cell-type specific innervation of the striatum (D1, direct pathway medium spiny neurons; D2, indirect pathway medium spiny neurons; PV, parvalbumin interneurons; ChAT, cholinergic interneurons) and unique patterns of connectivity with other basal ganglia nuclei. Black arrows, excitatory projections; red arrows, and inhibitory projections. (D) Connectivity of the thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN). (E) Relationship of three thalamic nuclei (limbic: AM; higher-order: Po; intralaminar: Pf) with respect to the patch (striosome) and matrix compartments of the striatum. (F) Connections of the zona incerta (ZI) that mediate interactions between the thalamus and basal ganglia. See the article text for references regarding the anatomical connectivity. Black arrows, excitatory projections; red arrows, inhibitory projections. APT, anterior pretectal nucleus; AD, anterodorsal nucleus; AM, anteromedial nucleus; AV, anteroventral; CM, centromedial nucleus; CL, centrolateral nucleus; DLS, dorsolateral striatum; DMS, dorsomedial striatum; Eth, ethmoid; GPe, globus pallidus external; LD, lateral dorsal nucleus; LGN, lateral geniculate nucleus; LP, lateral posterior; MGN, medial geniculate nucleus; Pf, parafascicular nucleus; PC, paracentral nucleus; PS, post-commissural striatum; PVT, periventricular thalamic nucleus; Po, posterior nucleus; SNc, substantia nigra pars compacta; SNr, substantia nigra pars reticulate; STN, subthalamic nucleus; TRN, thalamic reticular nucleus; VB, ventrobasal complex; VA, ventroanterior nucleus; VL, ventrolateral; VM, ventromedial nucleus; VP, ventral pallidum; VS, ventral striatum; VTA, ventral tegmental area; ZId, zona incerta dorsal; ZIv, zona incerta ventral.