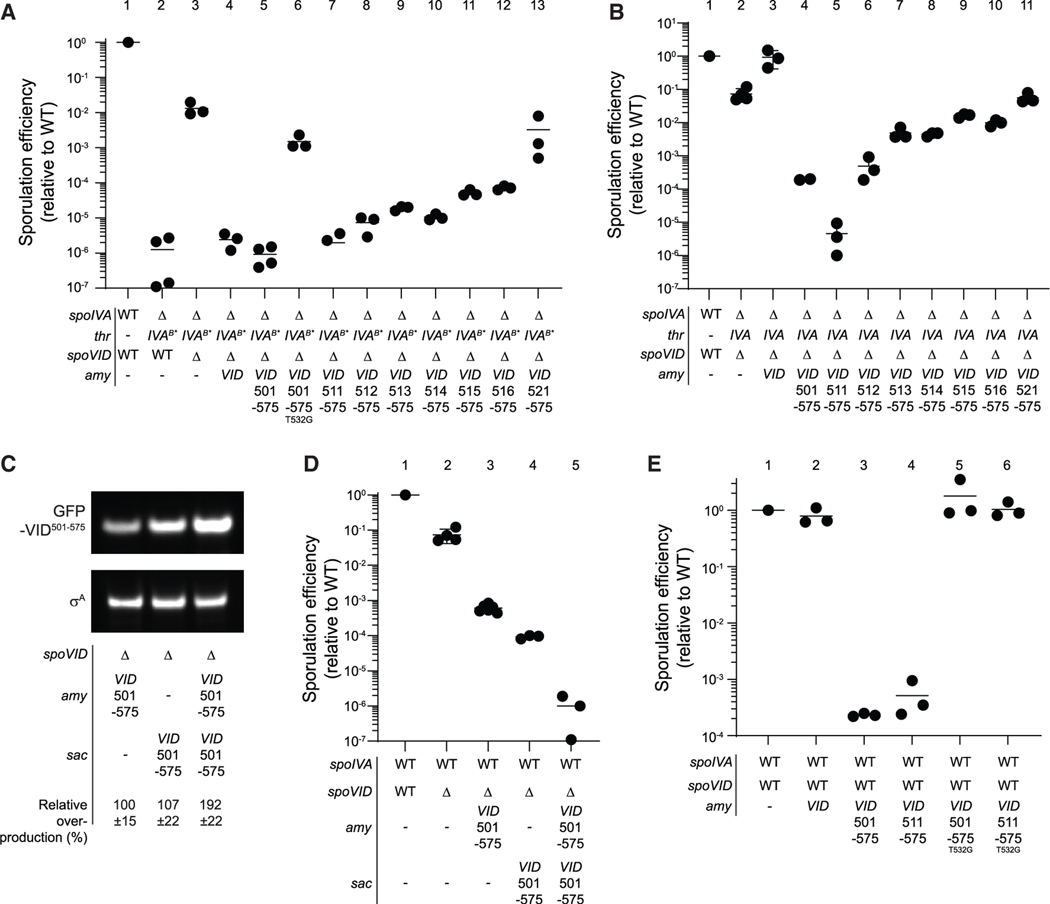
Figure 5. The carboxy terminus of SpoVID is sufficient for sporulation-inhibitory activity and is dominant-negative effect.
(A and B) Sporulation efficiencies of various strains, determined as resistance to heat, relative to WT (PY79). Strain genotypes at spoIVA and spoVID loci are indicated below the graph; thr and amy are ectopic chromosomal loci used to complement spoIVA and spoVID deletions, respectively, with different alleles of those genes. Strains used: PY79, JB103, JB280, TD139, TD931, TD955, TD996, TD998, TD999, TD1000, TD1001, TD1002, TD997, JB171, TD139, TD931, TD996, TD998, TD999, TD1000, TD1001, TD1002, and TD997.
(C) Representative immunoblot of cell extracts of sporulating B. subtilis cultures harboring a deletion of spoVID and expressing gfp-spoVID501–575 ectopically from either the amy (left), sac (center) loci, or from both amy and sac loci (right). Strain genotypes and relative overproduction of GFP-SpoVID501–575 as determined by quantification of immunoblots from three independent cultures are indicated below (errors are SD). Strains used: TD1070, TD1085, and TD1086.
(D) Sporulation efficiencies of WT, ΔspoVID, or strains in (C) producing GFP-SpoVID501–575. All symbols are independent cultures; bars represent mean values. Strains used: PY79, TD100, TD1070, TD1085, and TD1086.
(E) Sporulation efficiencies of strains harboring native copies of spoIVA and spoVID and expressing ectopically either GFP-SpoVID501–575 or GFP-SpoVID511–575, or GFP-SpoVID501–575 or GFP-SpoVID511–575 harboring a disruption in the LysM domain (T532G). Strains used: PY79, JB217, TD1029, TD1031, TD1030, and TD1032 (see also Figure S1D).