Fig. 2. Lung macrophages are key IL-9 responders in allergic response.
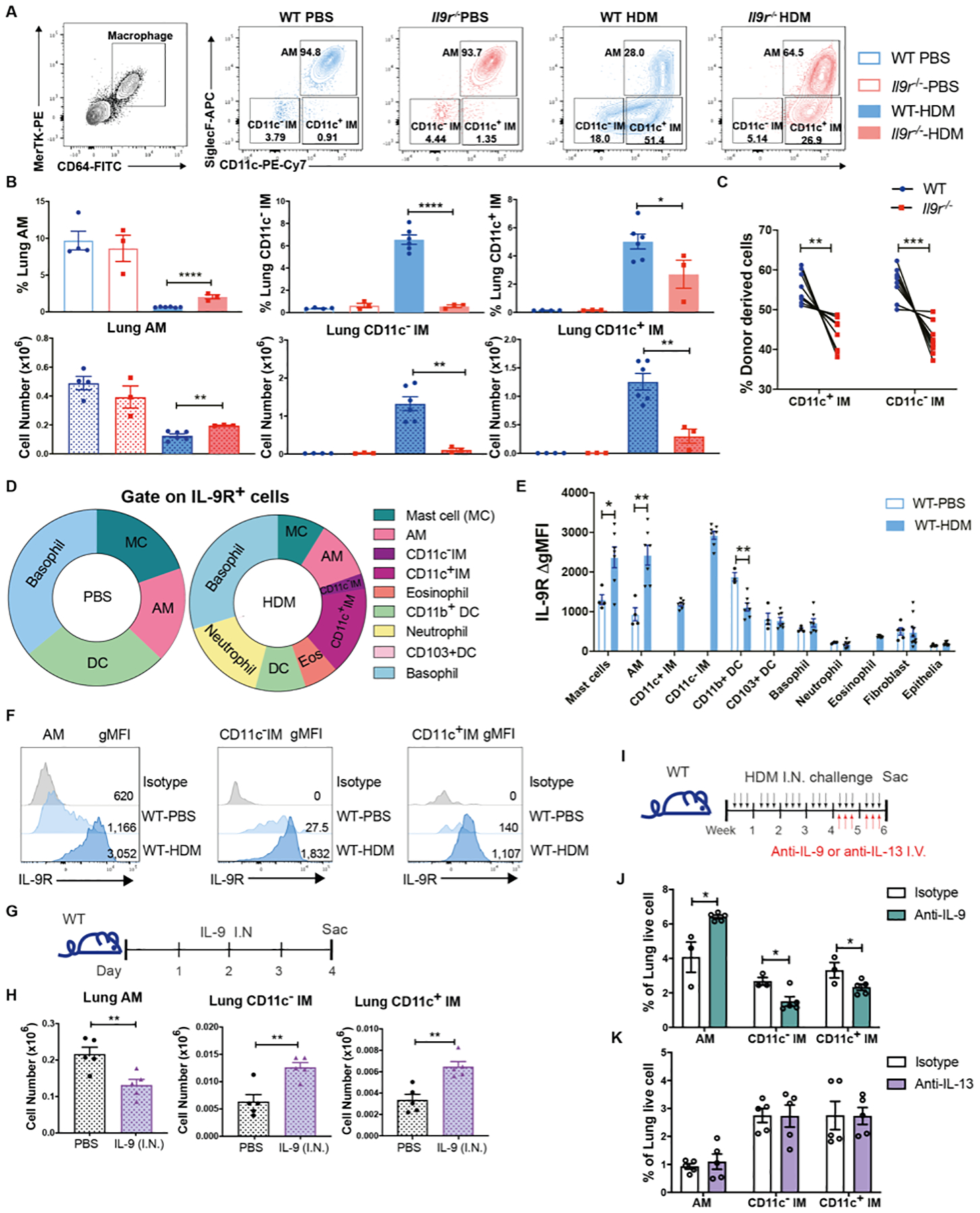
Mice were intranasally treated with HDM three times a week for six weeks.
(A and B), Flow cytometry analysis of lung macrophages (n = 3 for WT-PBS and Il9r−/−-PBS group, n = 6 for WT-HDM group, n = 3 for Il9r−/−-HDM group).
(C), WT (CD45.1) and Il9r−/− mice (CD45.2) bone marrow cells were mixed in 1:1 ratio and transferred to lethally irradiated recipient mice (CD45.1+CD45.2+ mice). After reconstitution, chimeric mice were treated with HDM, lung macrophages from donor cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 9).
(D–F), Lung cells from PBS- or HDM-treated mice were stained with IL-9R and other surface markers for analysis by flow cytometry. (D), Pie chart analysis of IL-9R+ cells. (E), Fluoresence intensity of IL-9R among various populations were analyzed, ΔgMFI is the gMFI of each population minus the gMFI of isotype controls in that population; there were too few IMs for analysis in PBS-treated mice (n = 4–7). (F), Histogram of IL-9R in lung macrophage populations.
(G and H), Mice were intranasally treated with IL-9 for three days (G). (H), Lung macrophages were analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 5 per group).
(I-K), Mice were treated with HDM for six weeks, anti-IL-9, anti-IL-13 or isotype-matched control antibodies were intravenously injected every other day during the last two weeks (I). (J and K), Lung macrophages were analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 3–5).
Data are presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed Student t-test was used for comparison to generate p values in B, E, H, and J. Paired two-tailed t-tests were used to generate p values in C. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001. See also Fig. S2.
