Figure 1. Pioglitazone inhibits chemical pain with greater potency in female as compared to male mice.
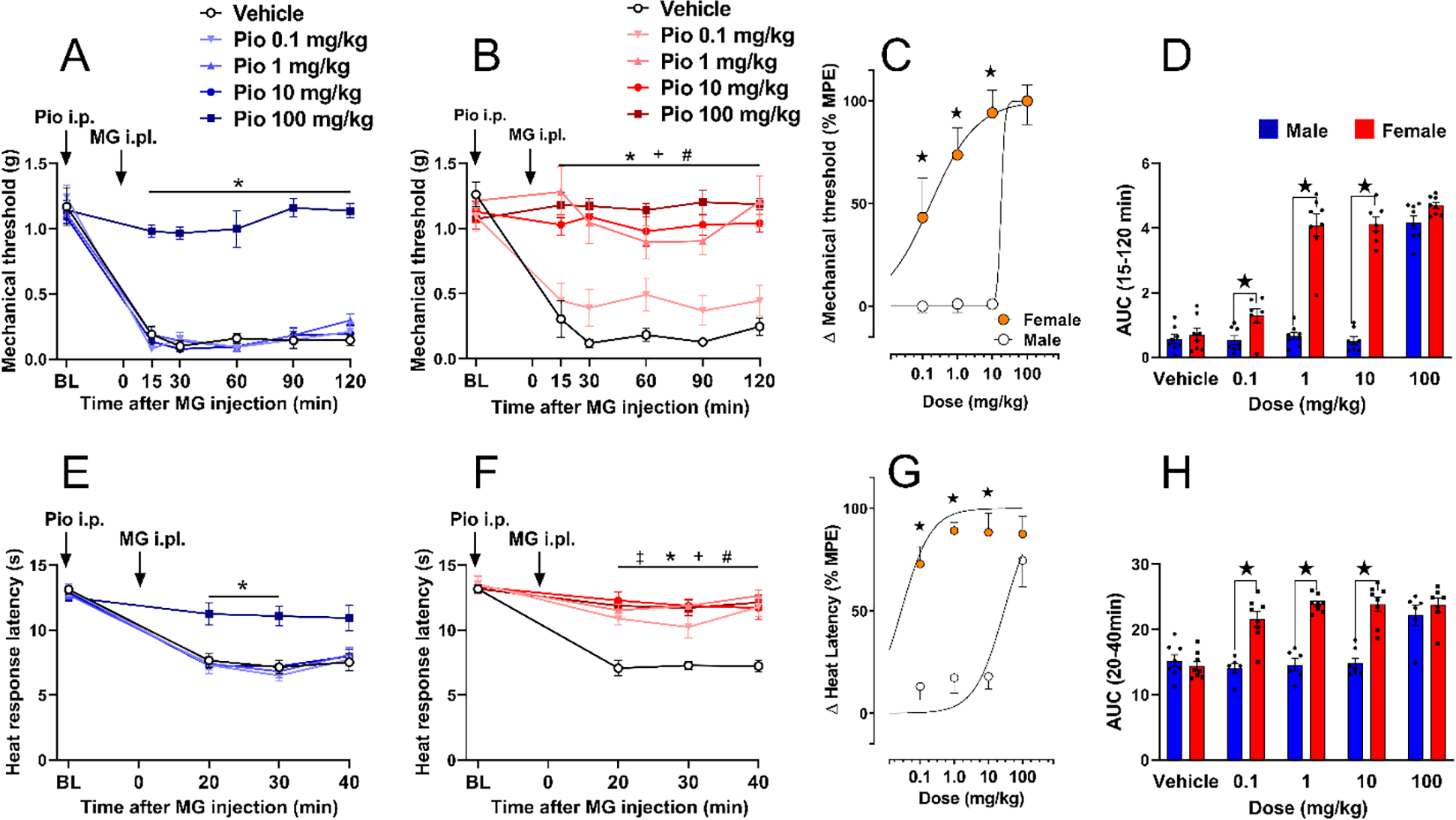
(A) Only the 100 mg/kg dose of pioglitazone prevented mechanical hypersensitivity in male mice. (B) 1–100 mg/kg pioglitazone decreased mechanical hypersensitivity in female mice. (C) Dose-response curve indicating that pioglitazone decreased MG-induced mechanical hyperalgesia in a dose-dependent manner with a greater effect in females (ED50: 0.17 mg/kg) as compared to males (ED50: 17.85 mg/kg). (D) Analysis of the data with Time collapsed across post-injection timepoints illustrates that pioglitazone exerted greater decreases in mechanical hypersensitivity in females as compared to males at 0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg. (E) Only the 100 mg/kg dose of pioglitazone prevented heat hypersensitivity in male mice. (F) Pioglitazone doses of 1, 10, and 100 mg/kg decreased heat hypersensitivity in female mice. (G) Dose-response curve showing that pioglitazone decreased MG-induced heat hyperalgesia in a dose-dependent manner with a greater effect in females (ED50: 0.028 mg/kg) as compared to males (ED50: 28.8 mg/kg). (H) Analysis of the data with Time collapsed across post-injection timepoints illustrates that pioglitazone exerted greater decreases in mechanical hypersensitivity in females as compared to males at 0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg. Two-way ANOVA was performed followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test for figures 1B–C, 1E–G and 1I. Non-linear regression analysis log(agonist) vs. normalized response was performed for figures 1D and 1H. %MPE = maximum possible effect. Symbol * P<0.05 Pio 100mg vs vehicleicle; + P<0.05 Pio 10mg vs vehicleicle; # P<0.05 Pio 1mg vs vehicleicle; ‡ P<0.05 Pio 0.1mg vs vehicleicle. ★ P<0.05 male vs female. Values represent mean ± SEM. N=6–8.
