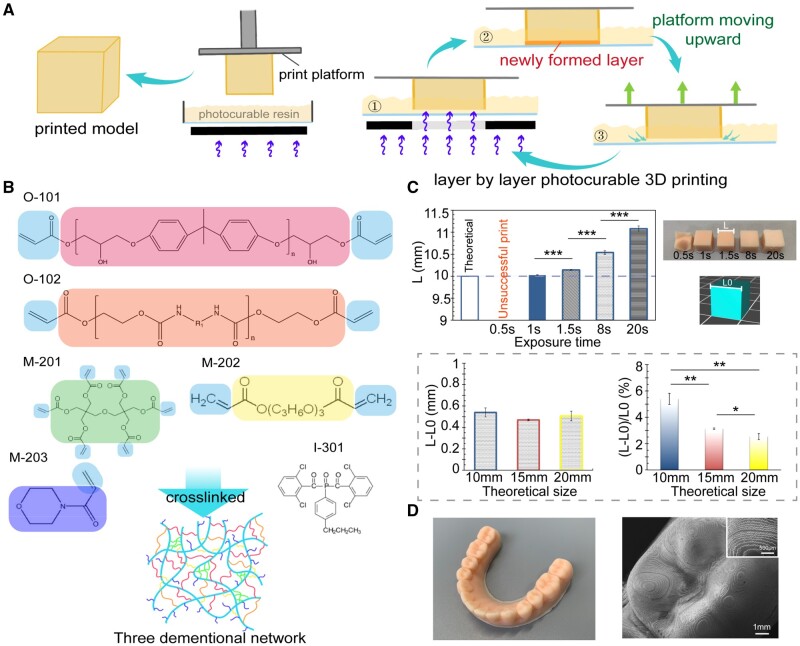
Figure 2.
3D printing via SLA to generate molds to eventually fabricate polymeric invisible orthodontic aligners. (A) Schematic diagram of the principle of 3D printing process with an LCD-SLA-type 3D printer. (B) Chemical structures of the photocurable resin components listed in Supplementary Table S1. (C) Histograms about the relation between the length of cubes and exposure time (n = 3). Photographs show the cubes with a theoretical length of 10 mm, which were obtained via printing with different exposure time. Diagraphs in the dotted frame show the absolute and relative deviations of lengths of cubes with different theoretical sizes at an exposure time of 8 s. (D) A global view and SEM image of a 3D-printed polymeric dental model.