Figure 4. Role of Tel1 at double-stranded DNA breaks and telomeres.
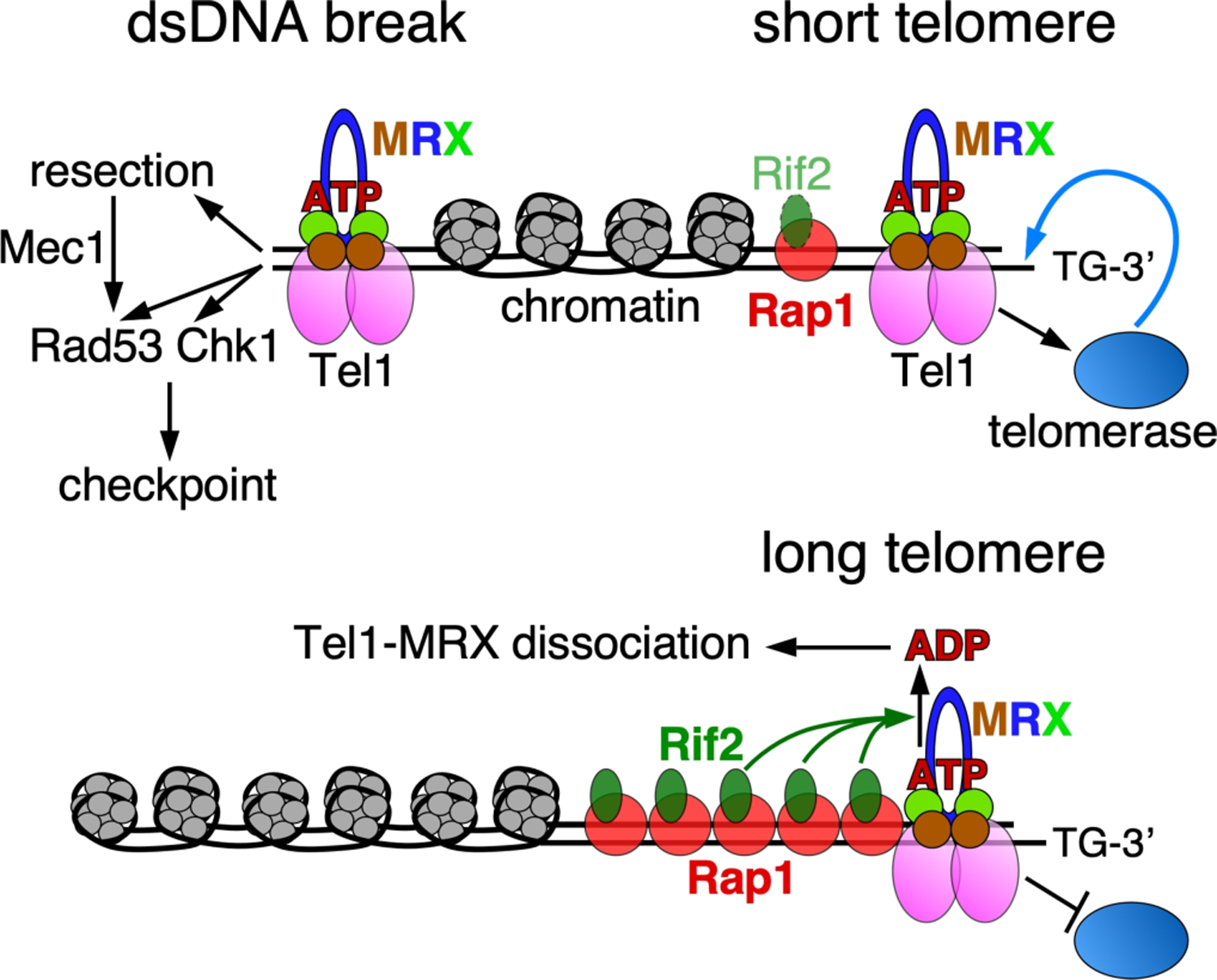
Damage-induced dsDNA breaks signal the recruitment of Tel1 by MRX. Only the ATP-form of Rad50 is competent for activation of Tel1. Activated Tel1 initiates a checkpoint by phosphorylating targets including Rad53 and Chk1. Tel1 additionally targets other factors that initiate DNA resection, which leads to a Mec1-dependent checkpoint response. Rif2 regulates telomere lengths by binding Rap1 and acting on Rad50. At a long telomere (bottom), the increased local concentration of Rif2 discharges the ATP-bound form of Rad50, thereby suppressing Tel1 activity, and promoting dissociation of Tel1 and MRX. At a short telomere (top), the relative lack of Rif2 allows Tel1-MRX activation of telomerase, resulting in telomere elongation.
