FIGURE 5.
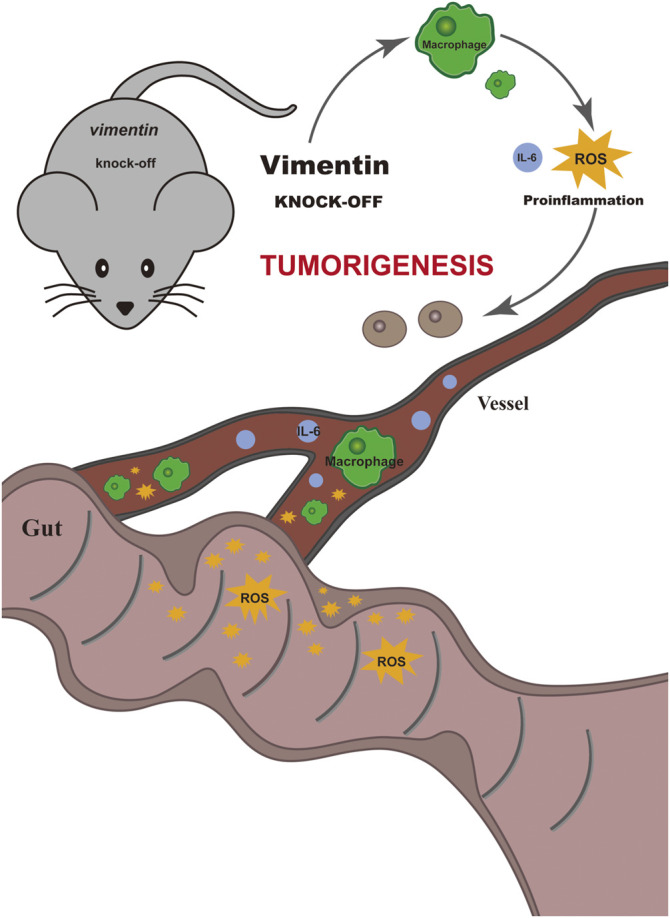
Schematic illustrate the mechanism of vimentin protecting the intestinal epithelium from inflammation and promoting tumorigenesis. The loss of vimentin in vivo leads to susceptibility to develop colitis-associated colorectal cancer upon the combination of AOM carcinogen treatment and DSS inflammatory injury, whereas the deletion of vimentin alone does not predispose to colitis-associated colorectal cancer.
