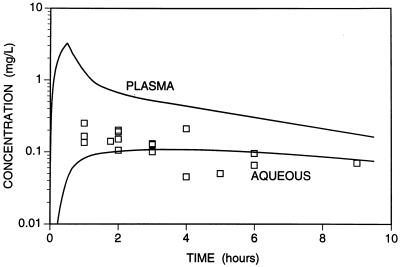
FIG. 4.
Time course of predicted concentrations of ciprofloxacin in serum and aqueous following cessation of an intravenous infusion (200 mg over 30 min). The time course of concentrations in serum were modeled from the mean kinetic constants after intravenous administration (distribution phase constant = 2.9 h−1, elimination phase constant = 0.179 h−1) (9, 13, 14). The concentrations in aqueous were predicted by using these kinetic constants and the mean rate constants of transfer of ciprofloxacin into and out of aqueous determined in the present study. The datum points represent the actual concentration in previous studies after intravenous administration (4, 16, 21, 24).