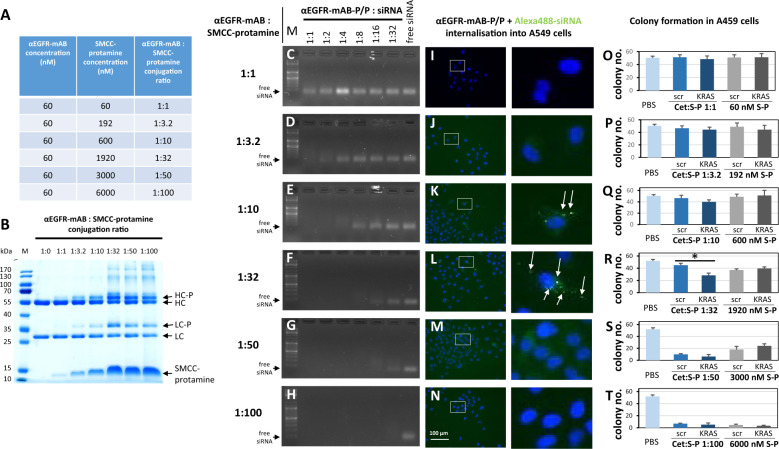
Fig. 1. Attributes of effective anti-EGFR-mAB-protamine conjugation ratios.
A Concentrations tested and resulting molar ratios of anti-(α)EGFR antibody (αEGFR-mAB) cetuximab to SMCC-protamine for the effective conjugation of both components. B Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE showing uncoupled αEGFR-mAB cetuximab compared to the conjugation products that were coupled as depicted in A. The formation of a protamine-conjugated heavy chain (HC-P) and light chain (LC-P) showed an optimum at a 1:32 conjugation ratio with no further increase at higher ratios. C–H Band-shift assays exhibiting siRNA binding capacity. I–N Internalisation of Alexa488-control-siRNA complexed by αEGFR-protamine and free SMCC-protamine (αEGFR-mAB-P/P) in A549 cells. Complexes of αEGFR-mAB-P/P transport Alexa488-siRNA into cells (left panel rectangles), with detailed magnifications (right panels). O–T Colony formation assays using the complexes analysed in C-H and I-N in EGFR-positive A549 cells. Significant effect of αEGFR-mAB-P/P transported KRAS siRNA effect in contrast to control scrambled (scr) siRNA is only seen in conjugate preparations with 1:32 molar ratio mAB to protamine (R). Conversely, lower ratios show ineffective binding of siRNA (C, D), do not internalise (I, J) and achieve no sufficient functional effect (O–Q), while preparations with higher molar excess of protamine-SMCC show toxicity independent of KRAS knockdown (S, T). A further selection of increments of coupling ratios between 1:20 to 1:40 were presented in Supplementary Fig. 2. Cet:S-P αEGFR-antibody cetuximab conjugated to SMCC-protamine at the indicated ratios, S-P SMCC-protamine. Mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Two-sided t-test, *p < 0.05.