Fig. 6.
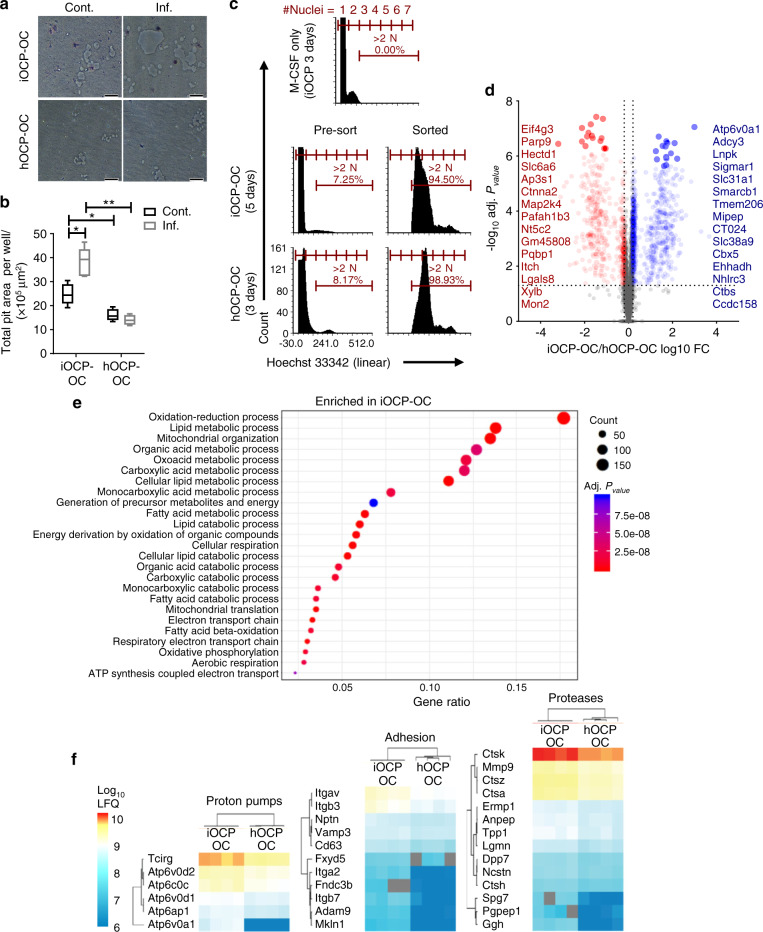
iOCP-derived OCs are more active and express more resorption-related proteins than hOCP-derived OCs. a Sorted iOCPs or hOCPs (5 × 104) from the BM of control and inflamed mice were cultured on Osteo assay surface plates in OC differentiation medium to generate OCs (iOCP-OCs and hOCP-OCs, respectively). The cells were cultured for 10 days until OC exhaustion (bar: 50 µm). b Total pit area per well represents the total resorption potential of a fixed number of precursors. n = 5 for each group, representative results for three independent experiments. Line: median, box: 25th–75th percentile, whiskers: range. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Mann–Whitney test and Holm multiplicity correction). c hOCPs and iOCPs sorted from the BM of inflamed mice were cultured for 3 and 5 days, respectively, with RANKL and recombinant M-CSF to generate iOCP-OCs and hOCP-OCs. The cultures were harvested, and mature OCs were sorted as cells with more than two nuclei identified by Hoechst 33342 staining. The threshold was set according to iOCPs cultured with only M-CSF for 3 days. d Top 15 differentially expressed proteins between iOCP-OCs and hOCP-OCs. e Enriched gene ontology biological process terms among significant iOCP-OC proteins. hOCP-OCs were enriched in only DNA replication (GO: 0006260). The Benjamini–Hochberg FDR was set to 0.05 for the GO analysis. f Expression heatmaps of OC activity-related proton pumps, adhesion molecules and proteases, which were significantly more highly expressed in iOCP-OCs. Four biological replicates were used (Limma, FDR = 0.05)