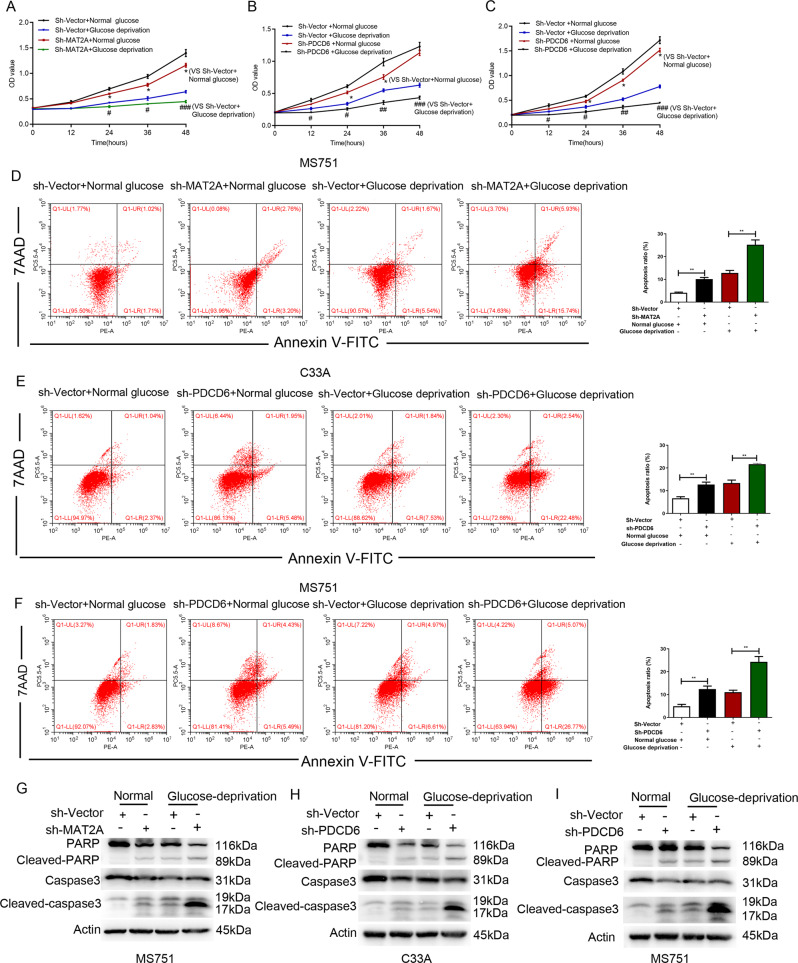
Fig. 2. PDCD6 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of MS751 cells.
A The proliferation of MS751 cells with or without MAT2A depletion was examined by CCK8 assay under normal or glucose deprivation. Error bar mean ± s.d. *P < 0.05. ###P < 0.001, #P < 0.05. B The proliferation of C33A cells with or without PDCD6 depletion was examined by CCK8 assay under normal or glucose deprivation. Error bar mean ± s.d. *P < 0.05. ###P < 0.001, ##P < 0.01, #P < 0.05. C The proliferation of MS751 cells with or without PDCD6 depletion was examined by CCK8 assay under normal or glucose deprivation. Error bar mean ± s.d. *P < 0.05. ###P < 0.001, ##P < 0.01, #P < 0.05. D Cell apoptosis of MS751 cells with or without MAT2A depletion was analyzed by Annexin V assay followed by flow cytometry (Left panel). Quantitative results were shown in Right panel. Error bar mean ± s.d. ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05. E, F Cell apoptosis of C33A cells (E) and MS751 cells (F) with or without PDCD6 depletion was analyzed by Annexin V assay followed by flow cytometry (Left panel). Quantitative results were shown in right panel. Error bar mean ± s.d. **P < 0.01. G–I Cell apoptosis was analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies under normal or glucose deprivation in MS751 cells with or without MAT2A depletion (G), C33A cells with or without PDCD6 depletion (H) and MS751 cells with or without PDCD6 depletion (I).