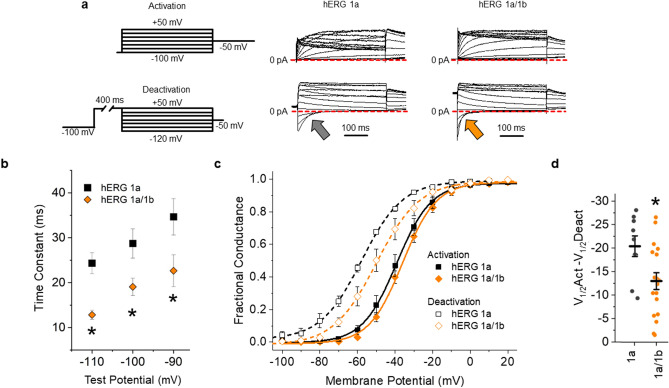
Figure 3.
hERG 1b expression reduces hERG channel hysteresis of ionic current. (a) Pulse protocol and corresponding sample ionic traces showing hERG 1a (middle) and hERG 1a/1b channel (right) activation when stably expressed in HEK293 cells recorded at physiological temperature (36 °C). (b) Pulse protocol and corresponding sample ionic traces showing hERG 1a (middle) and hERG 1a/1b channel (right) deactivation when stably expressed in HEK293 cells recorded at physiological temperature (36 °C). (c) hERG 1b modifies hERG channel voltage dependence. Normalized peak tail current, representing fractional conductance, is plotted as a function of pre-pulse potential and fitted with a Boltzmann function for hERG 1a (black) and hERG 1a/1b (orange). Channel activation recorded as in “(a)” is shown with solid symbols. Channel deactivation recorded as in “(a)” is shown with open symbols. (d) The magnitude of hysteresis was quantified by subtracting the V1/2 of deactivation from the V1/2 of activation. Hysteresis was significantly smaller in hERG 1a/1b heteromeric channels (n = 10) compared with hERG 1a homomeric channels (n = 7). All data are reported as mean ± SEM. * indicates p < 0.05.