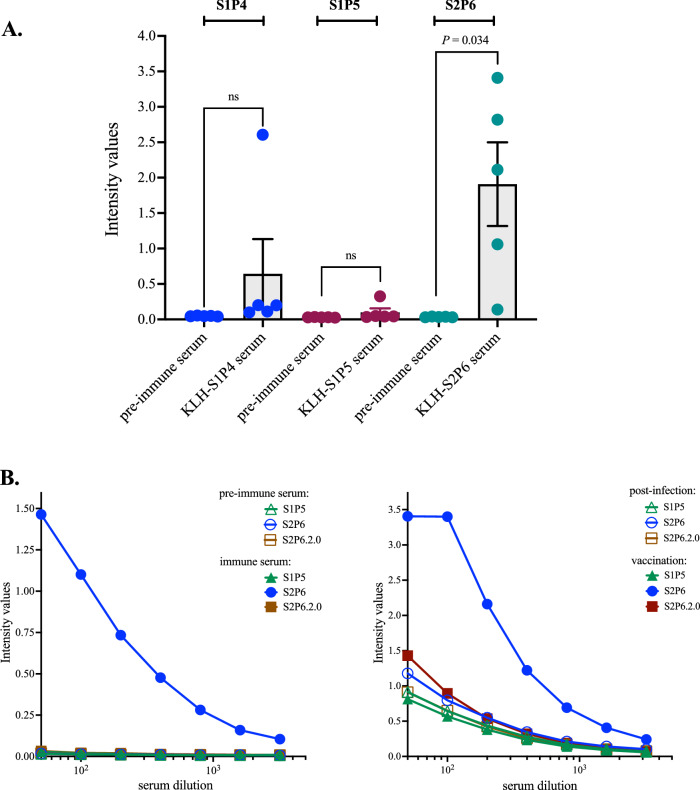
Figure 7.
Immune reactivity of mouse antibodies raised against B-cell epitope peptides. In (A), serum samples from mice (n = 5) that received the KLH-peptide conjugates were assessed for peptide-reactive antibodies through peptide-based ELISA using the synthetic S1P4, S1P5, and S2P6 peptides (200 ng.mL−1) for antigen-based antibody capture. The pre-immune serum of each individual that received the KLH-peptide conjugates was tested. The intensity values of serum samples at dilution 1:50 were measured at O.D. 450 nm. Paired t tests between pre-immune serum and KLH-peptide serum were performed (ns: non-statistically significant, p > 0.05). The results are representative of two independent experiments. In (B), synthetic peptide-based ELISA using the S2P6 and S2P6.2.0 peptides (200 ng.mL−1) for peptide-based antibody capture. At the left, pre-immune and immune serum samples of an immunized mouse with KLH-S2P6 conjugates. At the right, serum samples from a COVID-19 immune subject collected after recovery (post-infection) and after injection of a single dose of comirnaty vaccine (vaccination). Synthetic S1P5 peptide served as negative peptide control. The intensity values of serum samples in a dose-curve response were measured at O.D. 450 nm.