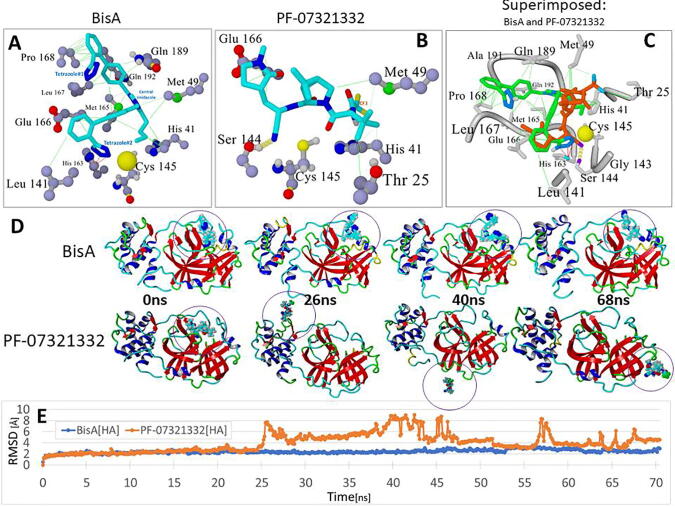
Fig. 8.
Comparison of docking motifs of BisA and Pfizer’s PF-07321332 antiviral drug with the Cys145 catalytic site of the main 3CLpro protease of SARS-CoV-2. (A) Details of BisA-3CLpro residue interactions. Ligand Atom Colors: C = cyan; N = blue; O = red. Tetrazole#2 of BisA interacted strongly with the His163 ring via pi-pi resonance (red lines). Tetrazole#1 exhibited no strong interactions, however, the biphenyl groups showed significant hydrophobic interactions (green lines) with several nearby residues, particularly Pro168. BisA did not appear to undergo direct interactions with Cys145, although BisA tetrazole#2 was proximal (3.74 Å) to the sulfur atom (large yellow sphere) and therefore probably interacted electrostatically. (B) As was the case for BisA binding, no direct interactions were observed between PF-07321332 and Cys145. However, it is noted that the –CN nitrile group was located proximal to the Cys145 sulfur, which is a potential site of covalent interaction with the ligand. Ligand binding was also marked by a strong hydrogen bond between the nitrile N and the Ser144 –OH. (C) Superimposed view of bound BisA and PF-07321332. (D) Frame captures at 0, 26, 40 and 68 ns from independent MD simulations of the BisA-3CLpro complex and the PF-07321332-3CLpro complex (drugs bound in the Cys145 catalytic pocket). MD conditions for both runs were: 311°K, NVT ensemble, 0.9 wt% sodium chloride (physiological saline), AMBER14 force field parameters. Bound PF-07321332 was unstable and exited the catalytic pocket beginning at about 20 ns, with complete extraction by about 25 ns. In contrast, BisA remained stably bound in the pocket for the duration of the 70-ns MD run. (E) RMSD values for: (1) BisA-3CLpro (blue line) and (2) PF-07321332-3CLpro complexes as a function of MD simulation time out to approximately 70 ns.