Extended Data Fig. 10 ∣. Comparison of the GR-Maturation Complex with the Hsp90:Kinase Complex.
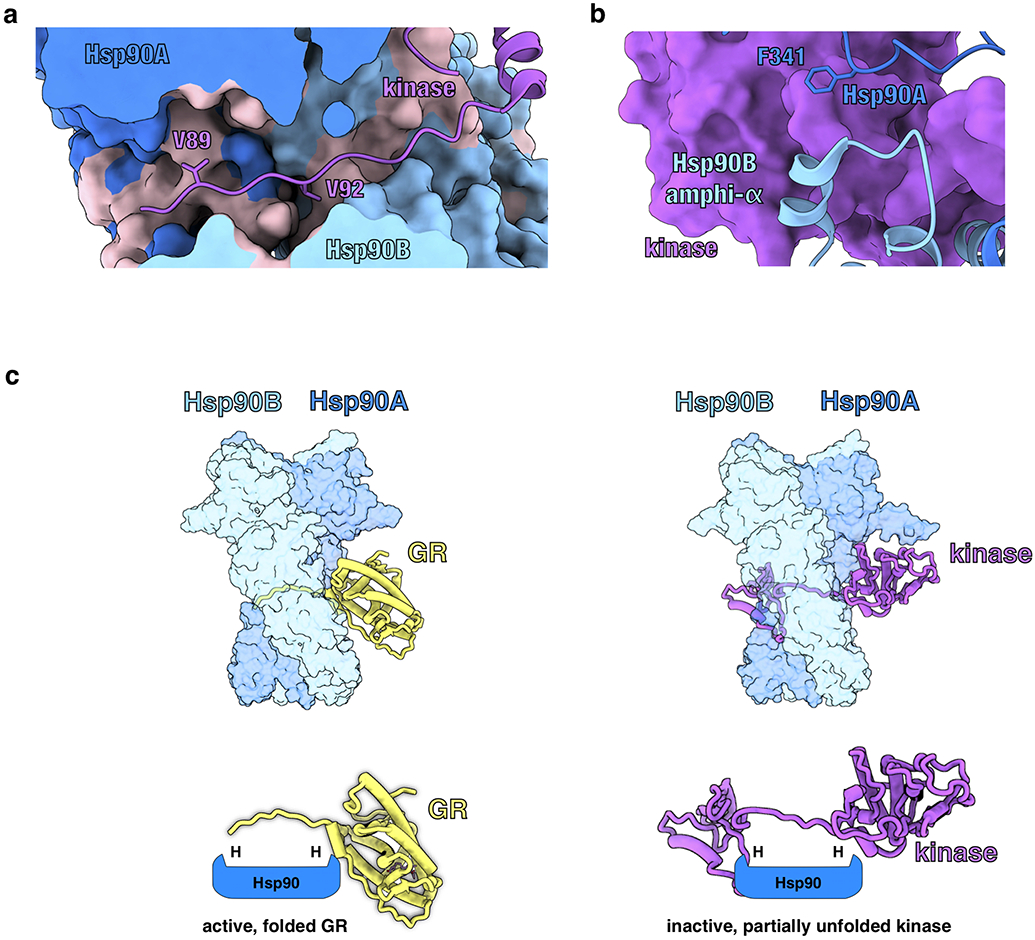
a, Structure of Hsp90 bound to an unfolded kinase client (PDB ID 5FWK) with a strand of the kinase client threaded through the Hsp90 lumen. The two hydrophobic residues on the kinase (Cdk4V89,V92) that occupy the Hsp90 hydrophobic pockets are displayed. In the GR-maturation complex, two hydrophobic residues on GR (GRL525,L528) occupy the Hsp90 hydrophobic pockets, demonstrating a conserved client binding mode. Hsp90A (dark blue, surface representation), Hsp90B (light blue, surface representation), Cdk4 kinase (purple). Hydrophobic residues on Hsp90 are colored in pink. b, Structure of Hsp90 bound to an unfolded kinase client (PDB ID 5FWK) depicting Hsp90AF341 (Hsp90 isoform β) and Hsp90Bamphi-α packing against the kinase. In the GR-maturation complex, the corresponding residue Hsp90AF349 (Hsp90 isoform α) and the Hsp90Bamphi-α also pack against GR, demonstrating a conserved Hsp90:client binding interface. Hsp90A (dark blue), Hsp90B (light blue), Cdk4 kinase (purple, surface representation). c, Top, atomic models of the GR-maturation complex and Hsp90:kinase complex showing that both clients thread through the closed Hsp90 lumen. Hsp90A (dark blue, surface representation), Hsp90B (light blue, surface representation), GR (yellow), Cdk4 kinase (purple). Bottom, schematics demonstrating that both clients thread through the mostly hydrophobic Hsp90 lumen, but have different folding outcomes (H=hydrophobic interface).
