Extended Data Fig. 4 ∣. GR is in a Native, Ligand-Bound State in the Maturation Complex.
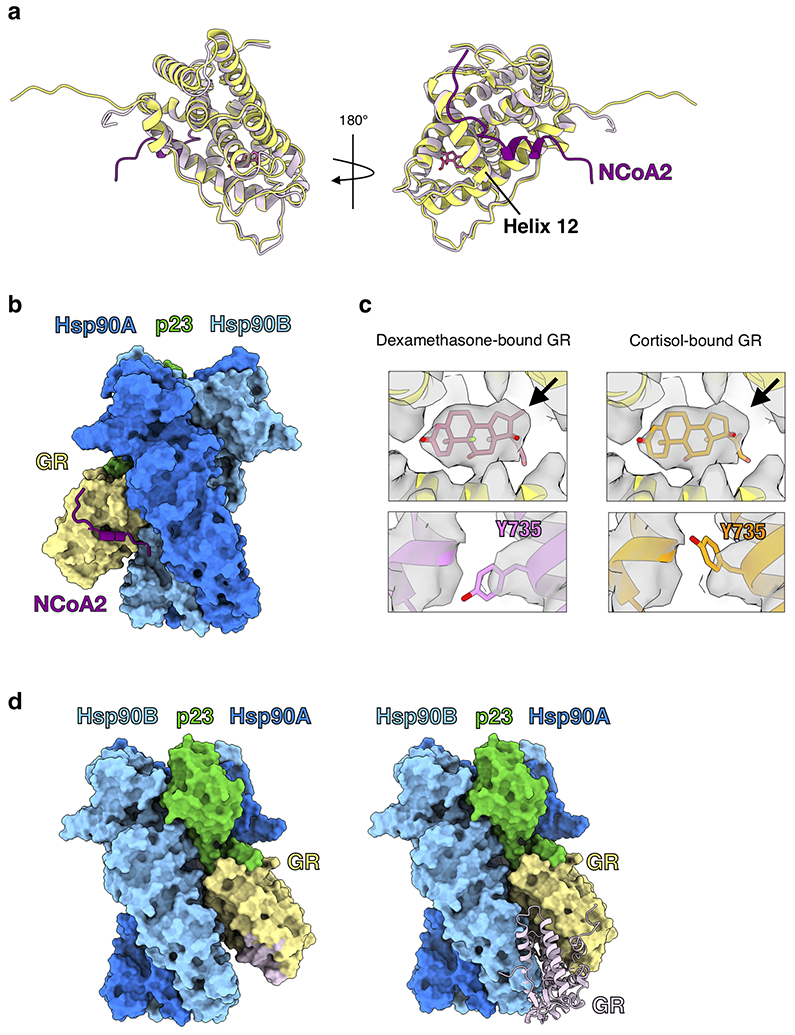
a, Atomic model of GR from the maturation complex (yellow) compared with GR from the crystal structure (PDB ID 1M2Z) (light pink) with co-activator peptide NCoA2 (purple) and ligand (pink). GRHelix 12 is indicated. b, GR-maturation complex atomic model in surface representation with the co-activator peptide NCoA2 (purple) docked based on the GR:NCoA2 crystal structure (PDB ID M2Z). The NCoA2 peptide binding interface is available and the bound NCoA2 peptide does not clash with Hsp90. Hsp90A (dark blue), Hsp90B (light blue), GR (yellow), p23 (green). c, GR maturation complex map density (sharpened with B factor −40) with either the dexamethasone-bound crystal structure docked (left panel, PDB ID 1M2Z) or the cortisol-bound crystal structure docked (right panel, PDB ID 4P6X) into the GR map density. In the top images, the ligand density is shown with the agonist dexamethasone (left) or the agonist cortisol (right) from the docked crystal structures. Arrow indicates the extra carbon atom in dexamethasone compared to cortisol. In the bottom images, density for GRY735 is shown with either the dexamethasone-bound crystal structure docked (left) or the cortisol-bound crystal structure docked (right). d, GR-maturation complex atomic model in surface representation depicting the GR LBD dimerization interface. Hsp90A (dark blue), Hsp90B (light blue), GR (yellow), p23 (green). Left, the GR LBD dimerization interface is highlighted (light pink). Right, while the dimerization interface is solvent accessible in the GR-maturation complex, the binding of a second GR LBD (light pink) clashes with the Hsp90B CTD. The dimerization interface is based on the GR LBD dimer crystal structure (PDB ID 1M2Z).
