Figure 2.
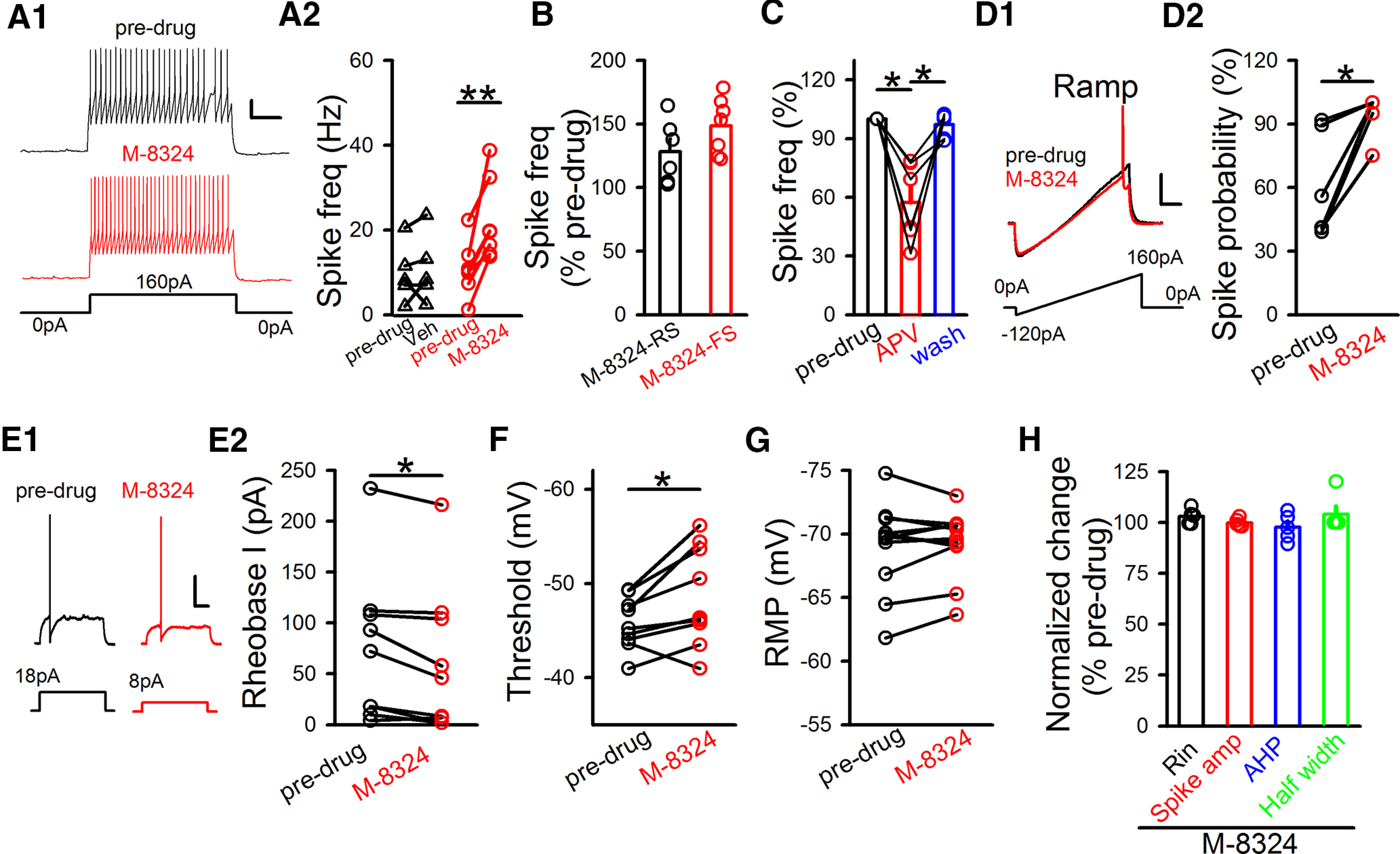
Impact of M-8324 on current injection-triggered spikes. A1, Sample traces represent M-8324's impact on spiking triggered by current injection in GABAergic neurons. Calibration: 200 ms, 20 mV. A2, Quantification of Veh and M-8324's impact after its application for 10-15 min. Predrug, 9.81 ± 3.07 Hz; Veh, 10.87 ± 3.58 Hz; RMP, −69.70 ± 0.21 mV, N (cells) = 5. Predrug, 10.84 ± 2.42 Hz; M-8324, 22.12 ± 3.64 Hz; RMP, −70.31 ± 0.43 mV, N (cells) = 7. **p<0.01 (paired t test). B, M-8324's impact on spike frequency in RS- and FS-GABAergic neurons. M-8324 (RS), 128.19 ± 10.13%; RMP, −71.71 ± 0.43 mV; N (cells) = 6. M-8324 (FS), 148.39 ± 8.34%; RMP, −70.5 ± 0.38 mV; N (cells) = 7. C, Impact of D-APV (5-10 min after application) on spike frequency on the same neurons. APV, 57.4 ± 8.2%; wash, 97.08 ± 2.44%; RMP, −68.96 ± 3.26 mV; N (cells) = 6. *p<0.05 (one-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni test). D, M-8324 increased spiking probability measured using a ramp test. D1, Sample traces. Calibration: 100 ms, 20 mV. D2, Population data. Predrug, 59.7 ± 10.07%; M-8324, 95.4 ± 4.08%; N (cells) = 6. *p<0.05 (paired t test). E, Reduced rheobase current in the presence of M-8324 in the same GABAergic neurons. E1, Sample traces. Calibration: 100 ms, 20 mV. E2, Population data. Predrug, 74.11 ± 24.49 pA; M-8324, 61.44 ± 23.92 pA; N (cells) = 9. *p<0.05 (paired t test). F, Threshold to spike was reduced by M-8324 application. Predrug, −45.77 ± 0.92 mV; M-8324, −48.59 ± 1.76 mV; N (cells) = 9. *p<0.05 (paired t test). G, M-8324 did not change RMP. Predrug, −69.03 ± 1.05 mV; M-8324, −69.24 ± 0.79 mV; N (cells) = 11. H, M-8324 did not affect basic neuronal properties in GABAergic neurons. Input resistance (Rin), 101.60 ± 2.21%, N (cells) = 5. Spike amplitude (spike amp), 99.90 ± 0.91%; afterhyperpolarization, 97.72 ± 0.91%; spike half-width, 105.41 ± 3.56%. Data are mean ± SEM.
