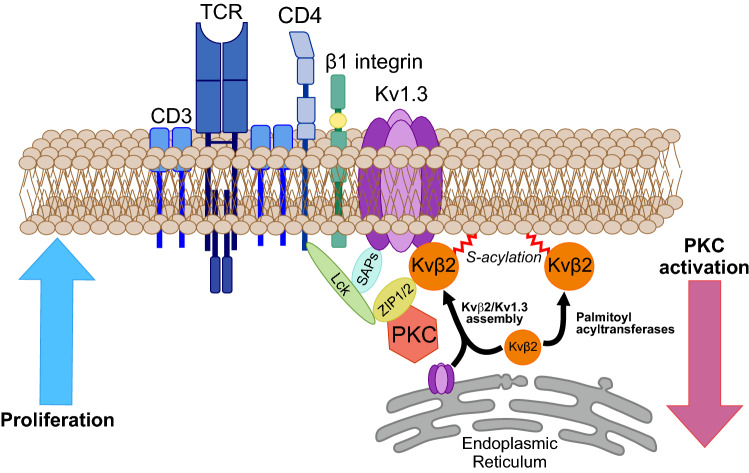
Fig. 10.
Cartoon representing the structural Kv1.3-associated proteins in the T-lymphocyte immunological synapse. The Kv1.3 channelosome merges a number of proteins modulating channel function at the IS during immunological synapses. PSD95 (also named synapse-associated protein 90; SAP90), which is encoded by the hDLG4 (discs large homolog 4) gene, stabilizes Kv1.3 at the IS. SAP97 (synapse-associated protein 97; hDlg1) plays similar roles. Therefore, SAP peptides bind to the PDZ domain in the C-terminus of Kv1.3, coupling p56lck to CD4. Kvβ2 links the N-terminus of the Kv1.3 channel to the ZIP1/2 protein, which may interact with several partners, such as p56lck and PKC. CD3 and Kv1.3 are in molecular proximity, and the channel interacts with β1-integrins. Our data indicate that ~ 10% of Kvβ2 targets to lipid rafts either associated or not with Kv1.3 and situate palmitoylated Kvβ2 (red sparkline) at the IS, independent of the Kv1.3 interaction, and stabilized by PSD95. Kvβ2 may link cellular metabolic activity and redox state with calcium signaling in lymphocytes. Kvβ2 also serves as a bridge with ZIP-1/2, which also links the complex to p56lck. Other proteins within IS are the T-cell receptor (TCR), CD3 and CD4 accessory proteins. Kvβ2 in activated T cells concentrates on the IS during synapse formation. Under proliferation, Kvβ2 targets lipid rafts, which are concentrated at the IS. In contrast, PKC activation triggers a lipid raft displacement of Kvβ2, which PSD95 counteracts