Table 2.
Examples of compounds in the highest activity group (group A1) shown with active substructures studied by means of substructure frequency analysis (depicted in red)
| Name of compounds | Structures of compounds and corresponding active substructure |
Purpose of use or distribution in nature |
Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4′4′-methylenedianiline |
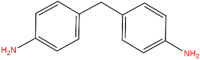
|
Food contact material | (U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2020a) |
| Quercetin |

|
A flavonoid (flavonol) in edible plants (e.g., onion) | (Chandra, 2010) |
| Genistein |

|
A flavonoid (isoflavone) in edible plants (e.g., soybean) |
(Chandra, 2010) |
| L-ascorbic acid |

|
Natural food substance; food additive |
(U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2020b) |
| L-Tryptophan |
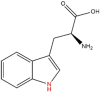
|
Natural food substance (amino acid) |
(U.S. Food and Drug Administration, 2020c) |
| Isoproterenol |

|
Drug; β-adrenergic receptor agonist (analogue of epinephrine) |
(U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2020) |
| Indole |

|
Food additive (flavoring agent) |
(Food and Agriculture Organization of the United States (FAO), 2020) |
| 2-Mercaptobenzothioazole |

|
Pesticide | (United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), 2020) |
| Phenmedipham |

|
Pesticide | (European Commission, 2020) |
| Azinphos-methyl |

|
Pesticide | (European Commission, 2020) |
| Dimethoate |

|
Pesticide | (European Commission, 2020) |
| Malathion |

|
Pesticide | (European Commission, 2020) |
