Fig. 3.
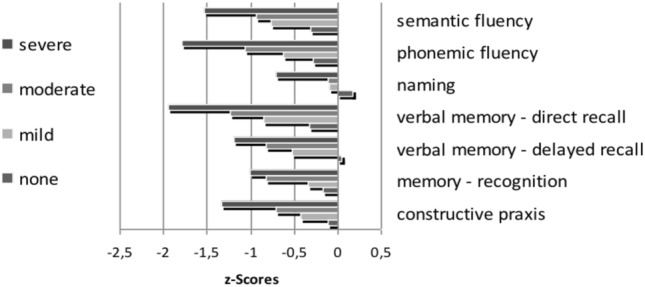
Group-by-time interaction effect (F(3, 239) = 3.196, p < 0.05), as shown by a different development of z-scores at one-year follow-up in relation to the grade of cognitive impairment at baseline (differences in z-values between baseline and 1-year follow-up). All domains reveal an impairment in cognitive performance. Bonferroni-corrected pairwise comparisons indicate that patients had the lowest scores in immediate recall (dr), phonemic (pf) and semantic fluency (sf),while no significant effects were found between those three (dr vs. pf: p = 1.0; dr vs. sf: p = .289; pf vs. sf: p = 1.0). All z-scores in the three tests were significantly lower compared to z-scores in the subtests of delayed recall (der; vs. dr: p < .001; vs. pf: p < .01; vs. sf: p < .05), memory recognition (mr; vs dr: p < .001; vs. pf: p < .01; vs. sf: p < .05), naming (na; vs dr: p < .001; vs. pf: p < .001; vs. sf: p < .001) and constructive praxis (cp; vs. dr: p < .001; vs. pf: p < .05). Only the difference between the semantic fluency and constructive praxis subtests failed significance. der: delayed recall; dr: direct recall, pf: phonemic fluency, sf: semantic fluency, mr: memory recognition, cp: constructive praxis, naming: na
